Decentralized information storage has been used since the 1990s. But after the success of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, distributed registries have become known beyond the realm of programming and computer applications. The principle of blockchain technology in simple words can be described as a database, which consists of many fragments and is stored simultaneously on different electronic devices.
In cryptocurrencies, this information relates to financial transactions, but with the help of chains, blocks with any set of characteristics (texts, contracts, pictures, music) can be fixed and transmitted within the network. The popularity of the technology is growing, so understanding it is useful for both traders and ordinary users.
What blockchain is in simple terms
The first information networks were centralized. Databases were stored on a common server and processed by a single node. This method of management had a significant disadvantage – the risk of hacking or technical failures on the main computer. In addition, there were risks of administrator misconduct in finance: banks, exchanges and exchangers had the power to block a customer, including for biased reasons. The Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain and other cryptocurrencies were designed to allow transactions to be processed in peer-to-peer (decentralized) networks in which community members have equal rights.
History
Developing a distributed storage protocol was a complex task. The unsolved problem remained protection against double-spending. If each participant processes transactions independently, the risk of deception increases: a user may send the same information to several counterparties or enter inaccurate information into the registry. The practical solution to this problem took more than 20 years.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 1991 | Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta published a paper titled “How to time stamp a digital document”. The authors presented the idea of using cryptographic algorithms to fix information about the date of its generation in the content of a data block. In this way, the document could not be rewritten retroactively. As a result, a chain of blocks was formed, which were placed in chronological order. |
| 1992 | Haber, Stornetta, and Dave Bayer developed a hash tree-based certificate of authenticity. This technology allowed the codes of previous blocks to be rolled up into a single document. A hash tree can be compared to the table of contents of a book, looking at which the reader is informed about the number and sequence of sections. |
| 1998 | Nick Szabo proposed the algorithm for the first cryptographic currency (Bit Gold). In this environment, the sender signs the transaction with a personal key. Each action is approved by the other participants. A new transaction can only be made after the previous transaction has been verified. The blockchain acts as a registry where transactions are grouped in chronological order. |
| 2008 | A whitepaper (technical description) of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency appeared on the Internet. The project allowed the transfer of money within a peer-to-peer network. To protect against double spending, users were assigned two keys: a private key (to confirm the transaction) and a public key (replacing the wallet address). Money could only be transferred sequentially from one holder to another. |
| 2013 | After the launch of the Ethereum project, users have access to smart contracts. Blockchain technology works like a database, but if you add command execution algorithms to wallet balance records, it becomes possible to enter into digital contracts. |
Distributed Ledger
The cryptocurrency blockchain stores transaction and wallet balance information. In centralized organizations (e.g., banks), this task is assigned to a server that hosts a single database. A distributed registry performs a similar function, but is duplicated on each of the computers connected to the network. The node updates the database by synchronizing it with other users.
5020 $
bonus for new users!
ByBit provides convenient and safe conditions for cryptocurrency trading, offers low commissions, high level of liquidity and modern tools for market analysis. It supports spot and leveraged trading, and helps beginners and professional traders with an intuitive interface and tutorials.
Earn a 100 $ bonus
for new users!
The largest crypto exchange where you can quickly and safely start your journey in the world of cryptocurrencies. The platform offers hundreds of popular assets, low commissions and advanced tools for trading and investing. Easy registration, high speed of transactions and reliable protection of funds make Binance a great choice for traders of any level!
Decentralization
The definition of blockchain as a database provides for the autonomy of each node connected to the network. If you analyze the structure of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, it is noticeable that none of the wallets are privileged. At the same time, blockchains of other projects may have a more centralized hierarchy. In some cryptocurrencies, transaction confirmation is entrusted to control nodes(nodes). But even in this case, payment processing is decentralized and performed simultaneously on multiple devices. This feature is important in terms of security and user trust.
The server of an ordinary bank, exchange, credit organization can be hacked or disrupted. Information in this case will be lost. If customers do not have paper documents confirming their ownership of the deposit, their savings may be lost.
In decentralized networks, the failure of one or more nodes will not result in the loss of financial information: the data will be retained by the other participants. Even if the world’s internet or electricity goes down, the blocks of the blockchain will not be destroyed. Important information will remain on physical media and will be restored after the outage is resolved.
The blockchain platform can work as long as at least one computer is connected to it. To destroy or tamper with data, most nodes would have to be taken over, which is nearly impossible for large projects like Bitcoin.
Protocol
Blockchain projects use different schemes of interaction between network participants. The order of information exchange and ways of confirming transactions make up the protocol written in the source code of the application. This can be compared to the rules of companies that operate on ordinary websites. If you read the user agreement in any Internet service, it will specify:
- Terms of registration on the site.
- Methods of order placement and payment.
- Term of delivery of goods or performance of work.
- Dispute resolution procedure.
The blockchain network is organized in a similar way. With the help of a protocol in it are established:
- Mechanisms (algorithms) of transaction confirmation.
- Type of data encryption.
- The size and frequency of formation of new blocks.
- The conditions of mining and the procedure for calculating rewards for confirming transactions.
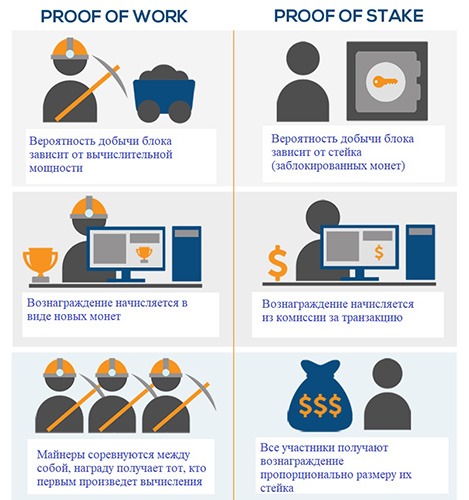
A key parameter of the blockchain protocol is the consensus (transfer verification) algorithm. This mechanism helps to determine whether a transaction is valid or not. A blockchain system can utilize such algorithms.
| Transaction verification method | Essence | Blockchain examples |
|---|---|---|
| Proof-of-Work (PoW) | To verify a transfer, miners must solve complex mathematical problems. The node that completes the calculation first is rewarded. The success of mining depends on the power of the devices used for block mining. | Bitcoin, Litecoin, Monero |
| Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Transactions are confirmed by those nodes that own the native coins of the network. The more cryptocurrency the “miner” has, the higher the chance that it is he who will be rewarded for the mined block. | Cardano, IOTA |
| Proof-of-Space | The value of the node depends on the amount of memory provided. To mine blocks, you do not need to perform mathematical calculations, but you need to allocate space on the hard disk. | SpaceMint |
Miners
The first cryptocurrencies (including Bitcoin) used the Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm. To get a reward, a miner had to repeatedly solve problems (calculate hash functions). This process can be compared to an accountant or auditor checking the records of several companies:
- The specialist compares the accounts of several companies and calculates their total balance sheet.
- If the data coincide, it means that there are no irregularities and the transactions are recognized as reliable.
- In case of a shortage at one of the companies, suspicions arise as to whether the employee who prepared the report has cheated. If there is such an assumption, the transactions between these counterparties are canceled.
Miners perform similar actions, but since the volume of information is very large, they have to use the computing power of computer devices (graphics or central processing units). To increase profits from block mining, special apparatuses – ASIC-farms – are created. This device looks like a beehive, in which instead of honeycombs inserted video cards. The computing power of farms for mining far exceeds the similar indicators of personal computers and laptops.
Nodes
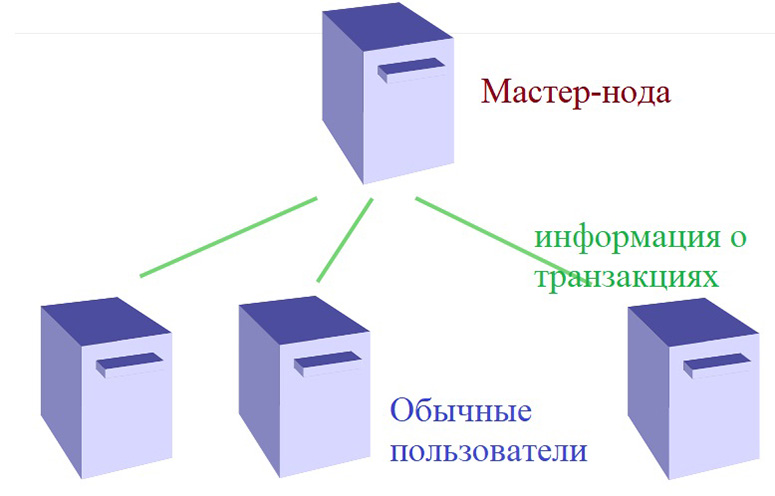
Since blockchain projects are peer-to-peer, they do not have a main (primary) server. A computer connected to the network can transmit information to other users. Accordingly, each device is an independent node (node). The computers of the participants are not always equal. Usually distinguish such types of nodes:
- Full. Contains data about all transactions that occurred between users.
- Light. It is needed for client access to transfers within the network. Does not contain complete data. An example of a lightweight node is a mobile device with a cryptocurrency transfer application installed. Through it, the client makes new transactions, but does not see information about past transfers.
- Privileged (masternode). Possesses extended rights in terms of transaction verification. In some networks, the masternode status is assigned to the most reputable wallet owners. You can become a privileged participant for a reward (a large investment in the project).
Creation and verification of new blocks
The purpose of cryptocurrencies is financial settlements between users. Therefore, blocks store information about the transactions made. If we describe this process in clear language, the creation of a blockchain looks like this:
- Miners select a certain number of new transactions to be entered into the blockchain. Requests with the highest fees are prioritized.
- After a certain period of time (about 10 minutes for Bitcoin), the selected transactions are added to a new block.
- The miners perform hash function calculations. If to explain on fingers, the process of transaction verification can be visualized as a comparison of data entered into the blockchains of different users. The correct chain is recognized as the one that matches the other participants in the network.
- After transactions are verified, a new block is assigned its own digital signature (hash). This cipher is used to determine the authenticity of the transactions included in it.
Types of blockchains
A distributed ledger can be used in different spheres of activity: finance, voting, data exchange between users. In this regard, there are several types of blockchains:
- Public. For dummies, this type of blockchain can be described as a public project that any users join. Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum.
- Private. In short, it is a closed community, registration in which is available only by invitation. An example of a private blockchain can be a decentralized voting application or the internal network of a private company.
In addition, exclusive (multi-level) blockchains are sometimes distinguished. In such networks, wallet owners have equal rights and free access, but only privileged participants can confirm transactions.
Private
Distributed databases are used not only as a means of payment, but also in other industries. With the help of blockchain technologies, they conduct voting, transfer files, conclude smart contracts. Closed (private) blockchains are suitable for these purposes. Access to registry records is granted only to individual clients. Within such a network, transactions are verified both by all participants and by a single, main server. Private registries have several advantages:
- Confidentiality. If the network is needed to transfer valuable information (personal documents, correspondence), only community members should have access to the chain.
- Speed of transaction processing. A transfer can be confirmed instantly by a separate masternode.
- Low costs. If there are no private miners in the network, it is not necessary to set attractive commission rates for them.
Public
The public blockchain is arranged as a fully decentralized network. Wallet owners have equal rights and can participate in verifying transactions and mining new blocks. There are several advantages of this type of registry:
- Protection from rash decisions by the administration. Each wallet owner can accept or reject changes to the source code proposed by the developers. This ensures the stability of the network.
- Broad access. Payment gateways, crypto exchanges and investment projects can attract users from different countries and constantly expand the client base.
- Trust. The essence of a public blockchain is the ability to verify the digital signature (hash) of each transaction. Customers replace any fraud in the chain.
Security of blockchain technology
The advantage of distributed registries is the inability of outsiders to change important information. This means that attackers do not have access to already mined blocks. Even if one node introduces unreliable data (a fake transaction) into the chain, the network will accept only those blocks that match on 51% of computers. The essence of hashing is that if at least one character is replaced, the function will be recalculated with a different result. As a result, the fake block will simply drop out of the chain, and the blockchain will return to its previous state.
Implementation in the Bitcoin system
An overview of distributed networks is usually made using Bitcoin, the most famous blockchain, as an example. The Bitcoin environment has these parameters:
- Transaction information is publicly published. Some sites store complete transaction data.
- Transactions are validated using the PoW method. Payments are verified by other users (miners) who provide computing power (ASIC farms or video cards) for this purpose.
- Digital fingerprints (hashes) are generated using the SHA-256 function.
- A new block is mined approximately every 10 minutes. The generation time is independent of the number of transactions. After the next 2016 blocks, the computational complexity increases. This protects the network from being taken over by large pools of miners.
The Bitcoin protocol is characterized by such pros and cons.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The possibility of mining. | High electricity costs for the operation of servers. |
| Tamper-resistant and popular encryption algorithm SHA-256. | Slow transaction processing. |
| Adjusting the complexity of calculations to protect against monopolization of the network by large pools of miners. | Low throughput. Records are updated every 10 minutes, with block size limited to 1 MB. |
Applications in society
Blockchain technologies are used not only as the basis of digital currencies. Distributed registries have these applications:
- Automatic contract enforcement. An algorithm that prescribes the terms of a transaction between two parties can be brought into the decentralized network. Such a contract, called a smart contract, is processed without the involvement of an administrator (intermediary), which guarantees the fulfillment of obligations. For example, the parties can prescribe an algorithm by which money is credited to the seller’s account only after he transfers a program or other asset to the buyer.
- Electronic voting. Decentralized voting applications are reliably protected from fraud and interference of interested parties. The citizen’s wallet is credited with a virtual coin that will be applied as a ballot. Data encryption makes it impossible to identify the participant, but at the same time anyone can see the election results.
- Copyright registration. The digitized code of a painting, app, or other intangible asset can be stored in the blockchain. This technology is called NFT (non-fungible tokens).
- Stock asset trading. Digitized stocks, bonds and other securities can be traded on a decentralized network.
Advantages of blockchain technology
Distributed databases have these advantages:
- Security. A registry entry cannot be tampered with. Hacking requires control over 51% of the connected computers. Even in the event of a major disruption (such as a natural disaster), valuable information will not be lost.
- Automation. Decentralized networks function without the involvement of administrators. Transfers are processed automatically.
- Low fees. The amount of the fee does not depend on the amount of the transfer. Since the volume of the transaction does not affect the speed of inclusion of the transaction in the next block, it is advantageous for users to use cryptocurrencies for large transactions.
- Anonymity. To create a cryptocurrency wallet, it is not necessary to confirm personal data. At the same time, blockchains are not completely anonymous: information about transactions is freely available. The sender or recipient can be identified by various parameters, including IP address.
- Uniqueness of information.
Security
Centralized projects have a vulnerable place – the main server. Sometimes, stealing the administrator’s password and transferring savings to personal accounts is enough to steal money from a bank or exchange. In cryptocurrencies, each wallet stores a separate copy of the block chain. Transactions are processed not by the server, but by other users, and the rights to digital currency are confirmed not by a password, but by a private key. Under such conditions, criminals can only hack into an individual computer, but not the entire environment.
Automation
As digital technology evolves, it will be possible to move to blockchain in many areas. Instead of a single database of customers, it is more convenient to connect them to a decentralized network. Their requests will be processed automatically, without necessarily collecting personal information.
Reduced fees
In some blockchain projects, miners do not participate in the confirmation of transactions. Counterparties pay a minimal fee to support the management servers (nodes). Unlike banks and private financial companies, cryptocurrencies have no owner. Therefore, some decentralized networks can operate on a non-commercial basis and allow counterparties to transfer currency for almost free.
Anonymity
Banks and financial companies verify the identity of customers. This information can get to attackers. In addition, financial legislation is gradually becoming stricter. A number of countries have adopted laws prescribing to block any transfers if their essence seems suspicious to the checker. Cryptocurrencies free users from restrictions and allow them to transfer money without attracting attention.
Uniqueness of information
The hashing mechanism prevents changes to already mined blocks. This protects the community from hacks and scams. Blockchain as the basis for cryptocurrency makes each coin unique. From the perspective of a coin owner, it may appear that the wallet holds regular electronic money. But because each transaction is signed with a hash function, all crypto coins are entered into a distributed ledger.
Disadvantages of the technology
Over the time distributed ledgers have been in use, 3 generations of decentralized protocols have been developed. Despite constant upgrades, blockchain technology is not without its drawbacks:
- Technical complexity. The simplest software is suitable for filling a centralized database. Joint work of distributed nodes is possible only if there is a protocol regulating the order of data encryption and block verification.
- Impossibility to cancel transactions. Even if a transaction is made by attackers, community members cannot stop the transfer. The information entered into the chain remains there forever.
- High electricity costs for the operation of the network. This disadvantage is characteristic of projects that use transaction confirmation using the Proof-of-Work algorithm.
- Legal uncertainty. The legislation of many countries lacks a description of blockchain technologies and digital currencies. This creates the risk of decentralized payment services being banned in the future. Users find themselves without protection from the state in case of wallet hacking or coin theft.
- The problem of scalability. According to a number of experts, blockchain technologies have now reached the limit of scalability. Their use in household transactions is impossible due to slow processing of transactions, the large volume of the blockchain. As an example, we can cite the average daily number of transfers in Bitcoin: this indicator almost did not change from 2018 to 2021.
Summary
Distributed registries have been used to store information since around 1991. The discovery of hash functions made it possible to create the digital fingerprints needed to protect data from spoofing. In 2008, the first blockchain project, the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, was launched.
Advantages of decentralized storage and processing of information:
- Security.
- Anonymity.
- Automatic confirmation of transactions.
Simultaneous operation of nodes in a peer-to-peer network increases energy consumption during mining. Users are also concerned about the irreproducibility of transactions, even if they are made after hacking or theft of digital money.
Frequently Asked Questions
❓ Which blockchain protocol is the most advanced?
Among cryptocurrency projects, Bitcoin holds the first place in terms of capitalization. But when it comes to technical aspects, many innovative protocols for decentralized networks have been developed in recent years.
✅ Can a distributed ledger be hacked?
Yes, such incidents sometimes happen. Hackers use the “51% attack” method (mass seizure of computers connected to the network). Attackers can also redirect user requests to fake hosts to steal private keys.
⛔ Do all cryptocurrencies have a blockchain?
No, only digital coins have their own registry. Another type of electronic assets – tokens – work inside the blockchain of other people’s cryptocurrency projects. For example, USDT and DAI are embedded in the Ethereum protocol.
❔ What consensus algorithms are common?
PoW or PoS methods are more commonly used in peer-to-peer networks. Hybrid variants that combine both algorithms have also been developed.
❗ How do government agencies view decentralized networks?
As of 2021, blockchain technologies are regulated at the level of law in many countries, including Russia. In some states (Ukraine, Kazakhstan) legalization of cryptocurrencies is being worked out.
Error in the text? Highlight it with your mouse and press Ctrl + Enter.
Author: Saifedean Ammous, an expert in cryptocurrency economics.