A decentralized network has a daisy chain structure. A block in mining is a key unit that contains transaction data. All crypto miners try to solve a complex computational problem to continue the chain and add new transactions to the blockchain. There is a reward for this by the algorithm. The miner also gets all the commissions from the transfers.
What is a block in mining
It is a software-generated structure with the necessary information for the decentralized network. Each new unit is added to the end of the chain. It cannot be removed or replaced because it contains information about the previous pieces. The process of building out is continuous. The editorial goes into more detail about creating a small piece of a large puzzle.
Why and how it is created
Each transaction with cryptocurrency is recorded in the registry. To put it there, you must first create a block. This is done by a computing device – a miner. It connects to the network and starts searching. The more devices mine cryptocurrency, the higher the complexity and potential profit.
Em que consiste
The block includes a lot of information. It usually consists of such elements:
- Magic Number. This is a number that contains specific values. They identify the block as part of the network of a particular cryptocurrency.
- Blocksize. Sets a limit on the size of the unit so that only a certain amount of data can be written into it.
- Block header. Contains information about the block.
- Transaction counter. A number that indicates how many transactions are stored in the block.
- Transactions. A list of all transactions.
The block header encrypts keys that contain information about the present and previous units of the chain. The step that brings the cryptocurrency transfer to completion is also recorded.
5020 $
bónus para novos utilizadores!
A ByBit fornece condições convenientes e seguras para a negociação de criptomoedas, oferece comissões baixas, alto nível de liquidez e ferramentas modernas para análise de mercado. Suporta negociação à vista e alavancada e ajuda os principiantes e os operadores profissionais com uma interface intuitiva e tutoriais.
Ganhe um bónus de 100 $
para novos utilizadores!
A maior bolsa de criptomoedas onde pode iniciar de forma rápida e segura a sua viagem no mundo das criptomoedas. A plataforma oferece centenas de ativos populares, comissões baixas e ferramentas avançadas para negociação e investimento. O registo fácil, a alta velocidade das transacções e a proteção fiável dos fundos fazem da Binance uma excelente escolha para os comerciantes de qualquer nível!
Size
The number of transactions in a block is affected by its size. For example, for the original Bitcoin network, it is 2 Mbytes. The structure fits a limited number of transactions. It also has a weight that affects its speed and cost. The larger the transfer amount, the heavier the transaction.
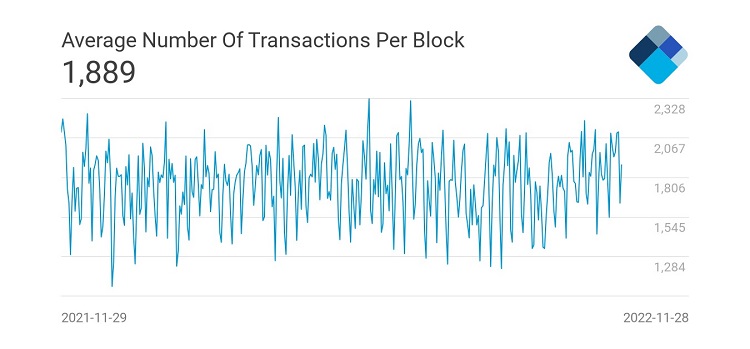
A 0.0001 BTC transfer will weigh approximately 226 bytes. The average number of transactions in one unit of the blockchain is 2,500. Bitcoin transfers are countless. A queue is formed to get into a new part of the blockchain. And the bigger it is, the higher the cost of commission in the network.
In November, for 1 transfer in BTC had to give an average of $1.6.
The introduction of Segregated Witness (SegWit) increased the size of the Bitcoin block to 4 Mbytes. The table lists the pros and cons of this update.
| Prós | Contras |
|---|---|
Empty blocks
The Bitcoin blockchain has a lot of computing devices running. They are busy searching for the next block in cryptocurrency mining. Once a participant has solved the problem and added a new element to the chain, the others start pumping in information. It is needed to compute the next structure. This takes some time, and power is wasted. That is why many people solve several tasks not step by step, but simultaneously.
Miners enter the first transaction (coinbase transaction) into the structure. It does not contain information about the previous part of the blockchain. It may be empty due to low activity in the network. This phenomenon was common in the early stages of Bitcoin. Now the trend is decreasing due to constant software improvements.
How to distinguish between identical blocks
Sometimes it happens that several miners in the same time solve the same computational task. There is a possibility of creating identical structures. The main chain begins to branch, new units of the blockchain may appear. Devices connected to the network favor a structure whose computation was more complex. If these were identical, computing devices choose the unit that was generated faster. Side branches are cut off, and all transactions therein are queued.
Autor: Saifedean Ammous, especialista em economia da criptomoeda.















