Today, the IT sector is developing new technology that will outperform any computing device by millions of times. The efforts of companies are focused in two directions: universal computers on qubits and devices for solving a single task.
After 2018, IBM introduced a quantum supercomputer for commercial use, and there were serious concerns among crypto market participants about the threat that computing machines based on this technology could pose. The fact is that a quantum computer and bitcoin are an ill-matched unity. The existing blockchain algorithm is vulnerable to a power that could, in theory, easily learn to crack cryptographic ciphers. What a traditional computer takes years to do takes seconds for quantum computing.

In 2019, the American Institute of Modern Science presented a list of 12 algorithms that are at risk, and among them are the most common in the crypto market – RSA, ECC. Therefore, the introduction of new types of encryption has already begun.
What are quantum computers
Traditional PCs work in a binary environment, where a bit – the smallest unit of information – can take one of two values: 0 or 1. All data is reduced to this form of sequential calculus. When solving a complex math equation, traditional computers take a lot of time.
Supercomputers use qubits – superpositions of an atom when it can exist in more than one state at the same time. That is, it does not take one of two values, but is the whole set at once.
5020 $
bónus para novos utilizadores!
A ByBit fornece condições convenientes e seguras para a negociação de criptomoedas, oferece comissões baixas, alto nível de liquidez e ferramentas modernas para análise de mercado. Suporta negociação à vista e alavancada e ajuda os principiantes e os operadores profissionais com uma interface intuitiva e tutoriais.
Ganhe um bónus de 100 $
para novos utilizadores!
A maior bolsa de criptomoedas onde pode iniciar de forma rápida e segura a sua viagem no mundo das criptomoedas. A plataforma oferece centenas de ativos populares, comissões baixas e ferramentas avançadas para negociação e investimento. O registo fácil, a alta velocidade das transacções e a proteção fiável dos fundos fazem da Binance uma excelente escolha para os comerciantes de qualquer nível!
The task, which is solved by a classical computer by sequentially going through combinations, takes years. A cubit processor performs calculations in a fraction of a second.
Princípio de funcionamento
Cubits function in a special way. The result of their activity is a matrix of variants from all possible answers, and the most probable one is the best. Cubits are of several types:
- Superconducting.
- Charge traps.
- Ion traps.
- Quantum dots.
Today, due to the level of technological advancement, many qubits can be created, but there is a problem – the instability of the system. The more fluxes used, the more errors occur in the computation. Superconductor qubits require cooling close to -273°C. For ion traps, superstrong magnets holding the atom in superposition. In both cases, complex systems require a lot of energy to operate.
Threat to cryptocurrency
Qubit computing makes it possible to solve problems millions of times faster than on today’s computers. The threat to blockchain lies in several aspects:
- 51% attack. An important element of the blockchain is the consensus method that validates transactions. If an attacker enters false information, it is rejected by other nodes in the network. In case a hacker gains control over more than half of the blocks in the network, this could be a problem. Theoretically, the speed of computation would make this type of attack more likely.
- Public keys. When a customer sends bitcoins to another person, they use their address. The recipient uses a private key to unlock the transaction. Just as knowing someone’s email does not give access to someone else’s account, a public key on the blockchain prevents this from happening. However, by computing in qubits, it is theoretically possible to hack wallets thanks to the inverse transformation.
Work on the transition to new encryption methods is underway among cryptocurrency creators and in government agencies that could be affected by an attack.
Cryptography and Shor’s algorithm
The point of encrypting information is to translate data into a sequence of characters in such a way that only the owner of the key can read it. There are already working prototypes consisting of hundreds of qubits that accomplish this task in a few years.
Reliability depends on the complexity of the reverse transformation by trying all possible combinations. For example, SHA-256 encodes information in such a way that it would take millions of years to decode consistently.
However, with the advent of Shor’s algorithm, solving such problems is greatly simplified, which could pose a serious threat to open-source cryptographic systems. Especially for blockchain, where the wallet address is compiled by transforming a private key.
The power of a quantum computer to crack the Bitcoin network
A processor consisting of 2500 qubits is needed to efficiently pick combinations of existing ECC code. The time interval when the computing power to attack Bitcoin can be achieved is about two decades.
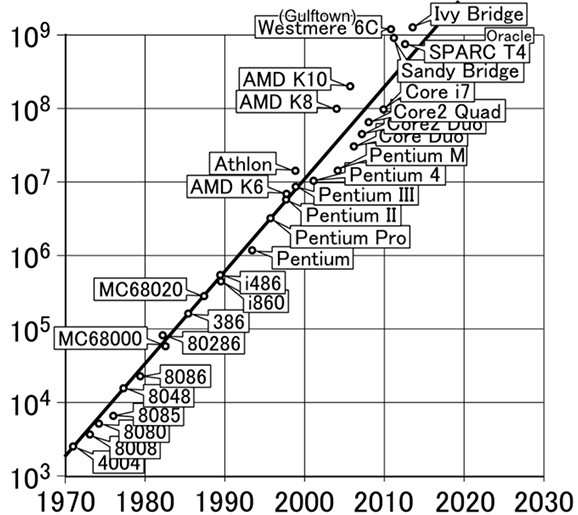
The most optimistic estimate is that by 2028, a machine will be created that will break a signature cipher in less than 10 minutes. Current systems are still far from that figure, but according to Moore’s Law, it could happen in 5-10 years. Today, a quantum computer for Bitcoin costs tens of billions of dollars, and it’s hard to imagine it falling into the hands of attackers. But the very fact that it could be hacked is alarming to owners of digital assets.
How the quantum computer affects cryptocurrencies
Analyzing the risks associated with the proliferation of fast-order computing has led to the beginning of research into new encryption methods that projects can switch to in the future to protect data.
As the cryptocurrency market continues to expand, it is important to realize that blockchain networks supporting digital coin transactions will be vulnerable to quantum attacks. The latter are relevant because of two mathematical approaches, the Shor and Grover algorithms. They enable computers to easily multiply large prime numbers, the basis of public-key cryptography, allowing encryption to be broken and data to be accessed. Before a quantum computer is created for Bitcoin, the entire industry will have already moved on to new stable algorithms for data protection.
Public Key
To perform the reverse conversion, hackers must possess the wallet address. It can be obtained in two ways:
- Decrypt the hash data in the blockchain.
- Gather information from the blockchain.
All transactions in the registry are viewable, and the client uses a private key to confirm the transfer. This way the system understands that the transaction is initiated by the owner. Having a wallet address, which is disclosed when transferring coins, using qubits it is possible to perform a reverse conversion and get the private key. If on a classic PC it takes a long time due to the low speed of selection, then, using a quantum computer, Bitcoin can be hacked in a few minutes.
Fast attacks
A potential vulnerability could be the time when the transaction has already been sent to the network, but has not yet been confirmed by miners or validators. Theoretically, during this period, it is possible to gain access to the protected information and change it (e.g., change the address or increase the transfer amount).
The significance of the time it takes to break encryption is that public keys are exposed when transactions are translated into the memory pool. This happens even before they are added to the blockchain. If an attacker unsubscribes and obtains the associated private key during this window period, they can broadcast the transaction at a higher fee, sending the coins to themselves.
The scenario described is the main reason why not reusing addresses without switching to another encryption algorithm is not considered a secure solution. That said, the threat of a quantum computer to Bitcoin is not immediate, and developers have plenty of time to think about the possibility of fixing vulnerabilities. This problem is already being addressed by high-bandwidth blockchains, where confirmations occur within seconds.
Reusing wallet addresses
In the world of cryptocurrencies, it is correct to say that users own the keys, not the coins. There are two of them in a wallet: a public, or address, which acts as an account number, and a private one, which the owner applies to transfer funds.
A hierarchical deterministic wallet (HDW) is used to ensure privacy. This method involves moving the balance of funds to a newly created address after the current private key is used to sign the transaction.
This reduces the risk of a quantum computer for Bitcoin gaining access to the wallet by converting the public address back.
Lost Coins
Since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009, when its price was a tenth of a cent, no one has thought about its future value. From the very beginning, digital assets were mainly interested in cryptocurrency enthusiasts. Having had enough of bitcoin, users forgot about it for years, until its rate began to grow. When the owners remembered about the coins, they often discovered that they had lost control over their wallets. This happened as a result of accidental deletion of a private key or hard disk failure.
A powerful computing center using Shor’s algorithm can restore access to the coins. According to various estimates, about 20% of the issued BTC are classified as lost. In 2021, their total value is more than $200 billion. Their sale could instantly crash the market.
Which cryptocurrencies are resistant to quantum computing
Preparation for the introduction of new technologies has not bypassed digital assets. Already today there are projects working on algorithms that will be able to resist the threat posed by new computers.
| Título | Descrição |
|---|---|
| This is a fully quantum-resistant blockchain network on the IETF cryptography standard. The company uses a hash-based extended Merkle tree signature scheme instead of an eliptic cipher, which is vulnerable to quantum attacks and is used in many blockchains. | |
| A digital asset that does not use cryptography and is based on a public key | |
| David Chaum’s project to create a cryptocurrency that is resistant to quantum computing |
Post-quantum algorithms and the future
Implementing such technology requires tweaking the infrastructure that already exists – in particular, switching to new encryption methods. Today, there are solutions that can secure bitcoin from the onset of quantum supremacy:
- Merkle Signature. Hash tree-based encryption.
- McEliece. One of the most promising methods based on error correction codes.
- Diffie-Hellman Protocol. Allows parties to exchange a cryptographic key through an unprotected communication channel.
So far, the threat posed by a quantum computer to BTC is very elusive. Even the appearance of a computing machine of the necessary size (2500 qubits) in the near future is not an unambiguously bad event. First of all, it will be used for the benefit of the whole civilization, calculating complex climate models, forecasting economic growth, solving unsolved mathematical problems, etc.
But if the most common encryption algorithm, ECC, is not replaced by the time the quantum computer becomes generally available, then humanity’s problems could be far more serious than cryptocurrency hacking and bitcoin theft using Shor’s algorithm.
Resumo
In the early days of cryptocurrency, blockchain networks relied on public keys that served directly as addresses for transactions. These translations are vulnerable to Shor’s algorithm, which can be targeted for hacking. This means that coins stored at any of these addresses could become accessible to attackers with the most powerful computers. A new form of blockchain transaction is public key hashing, which uses a one-way cryptographic function to break a public address into pieces. A computing machine will not be able to access the public key directly from the blockchain and therefore break the encryption.
The threat will arise when computers become much larger and more affordable than they are today. Fortunately, cryptocurrencies can be updated with forks to utilize post-quantum encryption standards and protect against these flaws.
Google announced a 150-cubit computing machine and made claims of achieving superiority over supercomputers. However, this ability to solve tasks faster than anyone else was shown only on one example with no practical application. It is still premature to talk about the beginning of a new IT era, because, besides the qubits themselves, a large infrastructure of systems and applications will be needed, which will take more than one year to build.
Perguntas mais frequentes
❓ What is quantum entanglement?
The correlation of qubits with each other, where a change in the state of one is reflected in another with no apparent physical connection between them.
❗ How is superposition achieved in computing?
By using very low temperatures to achieve the ability of superconductivity. This makes it possible to hold an atom under conditions where it simultaneously assumes all possible states. For example, a binary code can have both 0’s and 1’s at the same time.
🔧 Will blockchain hacking happen in the next 5 years?
Scientists agree that it will not materialize for at least a dozen years. Cryptocurrency developers have time to update protocols to encryption methods effective against a quantum computer for bitcoin.
💻 Can qubits be used for mining?
Theoretically yes, but then there will be a concentration of power in one hands, capable of a “51% attack”. By the time such computers become available, blockchains will have moved on to other methods of consensus.
💲 How will cryptocurrencies be updated?
With forks, new rules will be introduced into the network that will affect miners.
Há algum erro no texto? Realce-o com o rato e prima Ctrl + Entrar
Autor: Saifedean Ammous, especialista em economia da criptomoeda.















