The word means “fork, branching” in English. Fork is a modification of the original program code and a change of consensus. The result is a similar but separate coin. The new digital currency realizes the possibilities that the original asset was deprived of. If not all participants of the network agree with the changes, the tokens will exist in parallel. The article tells you what a fork of bitcoin and other cryptocurrency is. Since 2008, many versions of the Bitcoin blockchain have been created, but most did not become popular and were abandoned by the developers. However, Namecoin, Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold and a number of others continue to be developed.
What is a cryptocurrency fork
With the creation of the Bitcoin network, the digital coin industry began to develop. Goals and objectives emerged that required changes to the source code. In the segment of digital assets, the modernization of the protocol is called a fork. In this case, there can be both minor improvements of the blockchain and serious modifications. To adopt the latter, all network participants update the software.
If the community does not accept the innovations, the project is branched into 2 separate coins.
After the fork, the “old” blockchain does not disappear anywhere. It continues to work according to the new rules. But a parallel blockchain appears, which functions according to the old rules.
Why it is needed
In open-source cryptocurrencies, there is no central governing body that can single-handedly make changes to the protocol. A vote is needed to implement improvements. It involves code developers, miners and holders of full nodes. There are several reasons for the appearance of forks:
- Improvement of the characteristics of the coin. Developers sought to offer a network without the disadvantages of Bitcoin (low anonymity, poor scalability, high commissions). But the community opposed significant changes to the code created by Satoshi Nakamoto. Therefore, programmers began to launch separate coins.
- Changing the consensus algorithm. For example, in 2022, Etherium switched from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake. The old blockchain lost community support.
- Countering hacker attacks. An example is ETH and ETC. In 2016, attackers stole $50 million from the decentralized DAO protocol. In a vote, network members decided to roll back Etherium to a time when dApps didn’t exist yet. But not everyone agreed to this. Adherents of the classic modification of the network suggested using an older version of the blockchain. It was called Ethereum Classic.
Some users launch their own digital coins based on existing cryptocurrencies for marketing purposes. This is easier than writing code from scratch. Most of these coins have no fundamental value.
5020 $
bonus per i nuovi utenti!
ByBit offre condizioni comode e sicure per il trading di criptovalute, offre commissioni basse, un alto livello di liquidità e strumenti moderni per l'analisi del mercato. Supporta il trading a pronti e con leva finanziaria e aiuta i trader principianti e professionisti con un'interfaccia intuitiva e tutorial.
Guadagnate un bonus di 100 $
per i nuovi utenti!
Il più grande exchange di criptovalute dove è possibile iniziare in modo rapido e sicuro il proprio viaggio nel mondo delle criptovalute. La piattaforma offre centinaia di asset popolari, commissioni basse e strumenti avanzati per il trading e l'investimento. La facilità di registrazione, l'alta velocità delle transazioni e l'affidabile protezione dei fondi fanno di Binance un'ottima scelta per i trader di qualsiasi livello!
Storia dell'emersione
Shortly after the launch of Bitcoin, the developers became aware of the shortcomings of the first cryptocurrency. The block size was 1 MB, which was not enough for fast transactions on the blockchain. Therefore, in 2015, some team members proposed an update with improved scalability. They created a Bitcoin XT fork with an increased block size.
At the time of launch, only 12% of miners supported the new project, and a minimum of 75% of votes were required to adopt the changes. Community leaders spoke negatively about the novelty, so it was soon abandoned. Later, other developments appeared – in total, more than 50 Bitcoin forks were created. Some of them solved blockchain problems (such as low transaction speed, high commissions), others were launched for marketing purposes. The code of the novelties differed little from that presented in the original version. Bitcoin Unlimited, Bitcoin Classic, Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold, and Litecoin were the most popular.
Variations
The foundation of any cryptocurrency is the blockchain. The code can be written from scratch or based on an existing project. Forks, like different coins, have differences. Modification can be developed by any programmer. It is enough to change the characteristic and start mining.
The output will be a new digital currency, very similar to the original version. Some varieties can interact with the original chain, while others are incompatible with it.
Softforks
In the case of a soft fork, developers make non-critical changes to the protocol. This allows transactions to take place between the old and new chains. Miners use the available equipment to mine blocks. No parameters need to be adjusted.
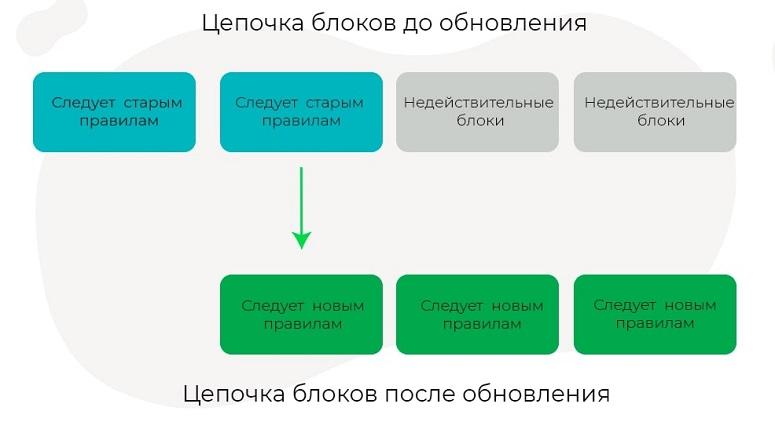
For example, you can reduce the block size in the Bitcoin blockchain. The updated nodes will filter information when confirming transactions and reject data larger than the specified parameter.
Classic
This is one of the “softest” ways to make improvements to the protocol. When creating a softfork, developers roll the network back a few blocks and modify. Users may not even be aware of the update. Nothing changes in the work of regular participants. Miners accept the version or continue to use the old one.
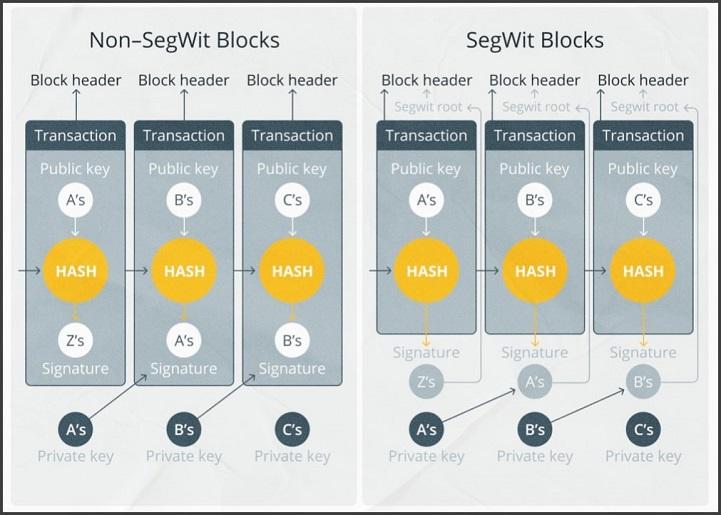
An example is the Segregated Witness (SegWit) softfork, which changed the format of blocks and transaction records. Each platform made the decision to support the new technology. Older nodes may validate the new blocks without understanding them. Such information is rejected. To read some fields, you need to use ordinary software.
User-activated
Classical softforces are launched by developers, but such authority is not necessary to make changes. The codes of bitcoin and some other cryptocurrencies are posted in the public domain. Any programmer can check them and modify them.
To run a softfork, the support of a major exchange or miner is required. In the case of APS-Fork (user-activated), the instructions are as follows:
- Make changes to the protocol.
- Make sure that everything works correctly and there are no bugs.
- Get support from a major exchange – for example, Binance. Or convince other major participants in the viability of the idea.
- Start a softfork.
While classic modifications are usually written by a group of developers, APS-Fork is a project that is handled by 1-2 programmers. Therefore, the task is much more labor-intensive. It takes a year or more to create and implement.
Hardforks
In some cases, changes are made to the protocol that are not compatible with the base version. The updated codes cannot accept transactions from nodes with old software. Therefore, the blockchain is divided into 2 – before the launch of the hardfork and after. If some users refuse to work with the new version and continue to support the old chain, the 2 coins function in parallel.
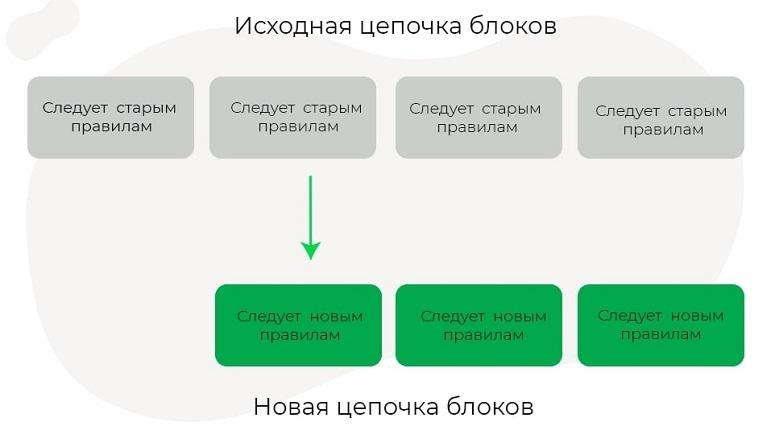
There will be no split in the community if the original chain will not be supported. Miners will have to buy new equipment. If all participants do so, the old cryptocurrency will devalue.
Planned
These are hardforks, accepted in advance by all participants. For example, Ethereum. The innovation (Merge) was prepared for several years. Everyone knew it was coming and waited for it. At the appointed time, miners started using the new version, and the old one was abandoned.
Controversial
When this type of cryptocurrency fork is introduced, there is a split in the community. Part of the users accept the improved version, while others continue to support the original coin. Both projects work in parallel.
Each cryptocurrency has its own team that can implement additional updates. At the same time, owners of the original coin retain the right to exchange assets for the new version.
Ethereum Classic is an example of a controversial blockchain fork. When the cryptocurrency was created, the community was divided. Some believed that it was necessary to reclaim the coins with a network hardfork. But others were not in favor of it.
Spin-off
This is the most “hard” type of modification. When a spin-off is launched, owners of old digital assets cannot claim new ones. In fact, another cryptocurrency arises, albeit on the basis of an existing one. Both coins develop in parallel.
The main differences between softfork and hardfork
Developers can make major or minor changes to the code. In hardforks, new rules contradict the previous ones, so the blockchain is divided into 2. Users have to choose which version to apply – the old or the proposed one.
The code modernization in softforks is not so significant. Updated nodes can work with nodes that have not accepted the changes.
How to determine security and reliability
Developing a fork is easier than writing new code from scratch. A promising coin emerges that is devoid of the flaws of the original. Some modifications managed to gather a strong community, and their prices increased tenfold.
But not all developers act honestly – some under the guise of updates release “pacifier” and stop supporting projects after their implementation.
There is also a risk of becoming a victim of a fraudulent scheme. For example, users receive an e-mail with an offer to invest in a new fork. But in the attached link there is a hidden virus, which transmits personal data of participants to attackers. Therefore, before investing money in the project, you should conduct your own analysis and do not respond to offers in personal messages.
Methodology for evaluating the project
Investing in new cryptocurrencies is always a lottery. Even if the project has a promising idea and a good team, no one will give a guarantee of its success. In fact, a fork is a separate coin, although similar to the original. It should be taken into account that many developers are interested in their own profit, not in the development of the crypto industry. Therefore, when deciding to buy, you should analyze the project. The criteria are as follows:
- Ilteam of developers. It is worth avoiding projects created by anonyms or unknown personalities. The probability of success of such startups is low.
- The popularity of the parent coin. High capitalization is an advantage when choosing a digital asset.
- Information about the fork. Developers must create a website, provide a presentation and technical documents.
- Listing on major platforms. It is good if the project is supported by influential exchanges.
You should also look at the project’s pages in social networks, assess the frequency of posts and their quality. It is worth investing in projects that meet most of the criteria.
Algorithm for obtaining coins as a result of a fork
Creating modifications is a labor-intensive work that requires programming skills, knowledge of the cryptocurrency code, and strategic thinking. At the same time, the process of obtaining coins as a result of softfork is simpler. To start, you will need a modern PC and access to IT services (GitHub, SourceForge). The algorithm is as follows:
- Download the source code of the cryptocurrency.
- Open a service for creating coins (for example, SourceForge).
- Insert the protocol and make changes.
- Fill in the specification of the new cryptocurrency – ticker, issue data, number of decimal places, consensus algorithm, block mining speed.
- Pay for the creation of the coin.
- Launch a marketing campaign.
In this way, you can create an improved copy of a working project. Success largely depends on the marketing strategy. It is necessary to create a strong community. To do this, you need to release a detailed white paper and disclose maximum information about the project.
Launching a hardfork is more difficult. Superficial programming skills will not be enough. The order of actions is as follows:
- Roll back the current blockchain by several thousand blocks.
- Make the necessary changes (consensus algorithm, block size or other parameters).
- Announce the launch time. Usually the block height at which the new rules will start to apply is announced.
The old cryptocurrency will continue to function. At the same time, the new version works at the same time. If the hardfork is planned – all participants update the software, if controversial – a split happens.
Popular forks of cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin gained widespread popularity and inspired developers to create altcoins. Some coins were written from scratch, while others were a modified BTC code.
Litecoin is one of the popular modifications of BTC. The cryptocurrency is faster and with lower fees than the prototype.
Later, LTC began to have its own offshoots – Dogecoin (DOGE), Monacoin (MONA) and others.
Since its creation, Litecoin has been actively supported by the community. The capitalization of LTC exceeds $4.9 billion.
Bitcoin softforks
To work with these modifications, you do not need to update full nodes. Therefore, users who are not interested in novelties may not even know about the next softfork. The most popular “soft” modifications of Bitcoin:
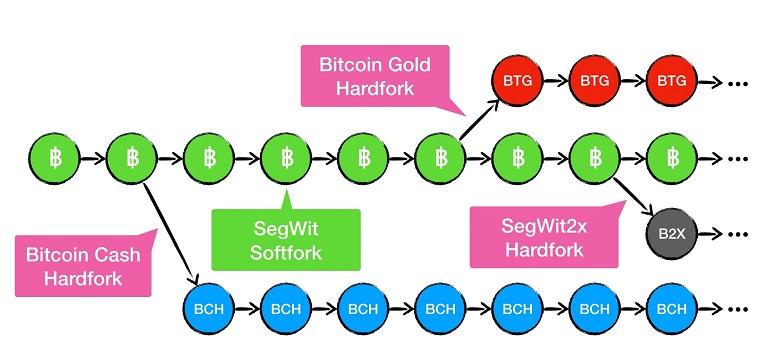
- SegWit. The update solves the problem of malleability and increases the speed of order processing. The block size in the Bitcoin blockchain (1MB) severely limits the number of transactions. Community members did not want to increase the blockchain as it significantly modifies Satoshi Nakamoto’s version. In 2015, Peter Welle proposed a different solution – some of the information was moved outside the block into a signature (Segregated Witness). This allowed more transactions to be transmitted simultaneously. The activation of SegWit caused a split in the community. Some participants stated that they would not support it. But it was not required. As a result, more than 90% of platforms installed the new software version.
- Lightning Network. To increase the throughput of the BTC blockchain, a second-level protocol with support for smart contracts was launched in 2018. The mechanism of operation – the user opens a channel to conduct micro transactions with a trusted person and a commission of 1 SAT. These transactions do not appear on the main network while the payment gateway is active. All transfers are then merged into one and transferred to the Bitcoin chain. This reduces the amount of data and shortens the processing time. With the Lightning Network, it was possible to maintain a high level of decentralization and security, reduce fees, and increase Bitcoin throughput. Softfork developer Joe Kenjiki assures that the potential of the add-on is not limited by anything. It can process more than a million transactions per second. The second-level network supports over 16 thousand full nodes. The technology is used by exchanges Kraken, Bitfinex, OKX.
Bitcoin Hardforks
Over the history of Bitcoin, more than 100 improved versions of the program code have been released. Since most of the community did not accept the changes, parallel coins appeared. Many have been unsuccessful. But some continue to evolve:
- Bitcoin Cash. This is the most popular BTC hardfork. The digital currency occupies the 15th line of the ranking in terms of capitalization. Compared to the original blockchain, Bitcoin Cash has higher transaction processing speed, lower commissions, and implemented the SigHash algorithm, which avoids double-spending of coins. In 2017, the hardfork increased the block size first to 8MB and then in 2018 to 32MB.
- Bitcoin Gold. The original blockchain has seen the difficulty of mining coins increase every year. Bitcoin has limited issuance and goes through halving every 4 years – reducing the reward by a factor of 4. The processing power of the blockchain is increasing (Bitcoin can only be mined on ASICs). Therefore, developers released Bitcoin Gold, in which they changed the consensus algorithm to Equihash. This allowed mining the coin on GPUs.
- Bitcoin Diamond. The cryptocurrency was released in 2017. The creators increased the maximum supply and block size. Unlike Bitcoin, transfers in the network are anonymous.
Forks of other coins
Bitcoin is the first and most popular cryptocurrency, so most developers modernized its code. But there are forks of other coins as well. The most famous ones are:
- Ethereum Classic. After stealing over $50 million from dApps DAO, the creators rolled back the network to a time when the project didn’t exist yet. More than 2 million users voted against the decision. These holdings continued to leverage the original blockchain, which was renamed Ethereum Classic (ETC).
- Monero. This is a successful fork of the Bytecoin cryptocurrency. With its help, the developers sought to solve the problem of BTC anonymity. Before listing, it was discovered that many blocks have already been mined.
Whether it is worth investing in fork projects
According to statistics, units of relaunched cryptocurrencies become successful. The most common reasons for failure are:
- Lack of community support. Before buying, you should evaluate how often the ticker is flashed in the posts of popular bloggers and forums.
- Weak team. Famous crypto-enthusiasts have more prospects. Trust in the team and the quality of the marketing campaign are important.
- Few advantages. Sometimes in practice, digital currency does not have the characteristics stated in the presentation and does not differ from the original.
It is necessary to realize the risks of investing in new projects. Investments can bring multiple profits or losses. It is worth buying the most promising forks for a small part of the capital.
Some developers hold airdrops – give coins to holders of the original asset. It is worth using such opportunities.
You can learn about future blockchain forks from the news. It is necessary to follow the pages of various cryptocurrency projects in social networks
How miners earn
Many forks are mined on the same equipment as the original coin. The complexity of the network in the updated cryptocurrency is much lower, so you can get more assets. Earnings are secured even with a minimum hash rate.
The miner takes a risk – if the project is not successful, the cryptocurrency can not be sold on the exchange. But if the team gathers a strong community, quotes will grow tenfold.
But sometimes cryptoassets that appeared as a result of forks use other hashing algorithms. In this case, similar hardware may not be suitable.
Implications for the network
Fork allows developers to improve the protocol – to solve known security problems, increase the anonymity of operations, scale the chain and reduce commissions. But there is a risk – modifications can be created by any programmer. A useless coin will not arouse the interest of serious investors. But due to a good marketing campaign, a fork can become popular among newcomers who do not understand the issue. This reduces the credibility of the industry among institutionalized investors.
Typical misconceptions of users
Dozens of new projects appear every day. Many of them are forks of well-known cryptocurrencies. Despite the clear startup technology, there are several typical user misconceptions about cryptocurrencies:
- To get a new asset, it is enough to keep the original one in your wallet. This is true if the tokens are stored on an exchange that supports upgrades. Otherwise, the cryptocurrency will not be credited.
- Fork coin must be transferred to the same address as the original. This is possible only in some projects when using a non-custodial wallet. It is more reliable to get a separate address for each cryptocurrency.
All forks will grow after the launch. In the first minutes after listing – probably yes. Further prospects depend on the features of the digital currency and the work of the team. A small number of coins go to the top.
Pros and cons of forks
Developers can not provide for all changes in the roadmap of the project. Therefore, the activation of forks helps to quickly introduce the necessary options and solve security problems. Updates have both pros and cons.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
Domande frequenti
❓ What is the timeframe for investing in hardforks?
Experts believe that the growth in the value of a promising coin occurs 6-18 months after listing. After that, the probability of a quote increase drops sharply.
📌 Where to get information about upcoming “forks”?
Up-to-date data is published by monitors (Coins Calendar, Coindar). Often forks are launched by independent developers. Therefore, there will be no information on the site of the original coin.
🧾 How many Bitcoin hardforks have there been?
Since 2009, more than 100 modifications have been released. However, only a fraction of them are functioning.
💰 Is a cryptocurrency hardfork a forced measure?
In most cases, yes. Developers make changes because of growing problems in the network. But sometimes hardforks are spelled out in the roadmap.
💡 How do you get new coins after branching the chain?
The easiest way to do this is on large centralized exchanges. Cryptocurrency is credited to holders of the original coins automatically.
C'è un errore nel testo? Evidenziatelo con il mouse e premete Ctrl + Entrare
Autore: Saifedean Ammous, esperto di economia delle criptovalute.