
In times of rapid development of the digital economy in the society, the issue of realization of cheap and fast payments, opportunities for different categories of population to use financial products is becoming more acute. Work is underway to increase the sustainability of business development and banking services, as well as to simplify cross-border transfers. New virtual forms of money can close these problems. However, the introduction of a national cryptocurrency requires significant investment as well as difficult policy decisions. Some countries have already adopted digital assets as a national cryptocurrency. This virtual money is safe, easily accessible and cost-effective. However, the risks and costs so far outweigh the potential benefits.
Why countries are creating a national cryptocurrency
Central banks are considering issuing virtual money in the form of digital obligations posted in their own name. Private companies, on the other hand, are pushing the boundaries by offering cryptocurrencies whose price depends on the security and liquidity of ancillary assets (e.g., stablecoins).
If bitcoin or altcoins were granted legal tender status, creditors would have to accept them as payment for monetary obligations. However, coins and tokens are unlikely to take root in countries with stable inflation, hard currencies, and sound financial institutions. Businesses have no incentive to set prices for goods and services denominated in an asset like bitcoin. Cryptocurrencies are too volatile and their price is not linked to the economy.
The term “central bank digital currency” (CBDC) has begun to attract the attention of governments, financial organizations, and developers.
Digital central bank currency, or virtual fiat money, is no different from cash units of account, except that it is in virtual form. Unlike private coins and tokens, government cryptocurrency is a centralized legal tender issued by a country’s bank.
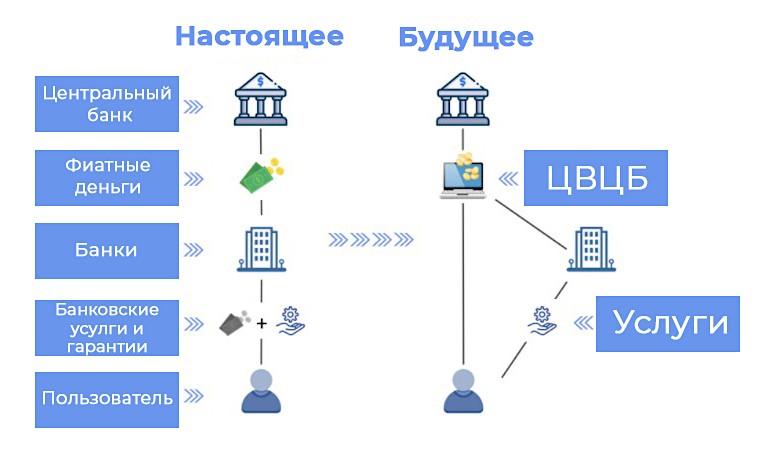
Depending on a state’s economic situation, the International Monetary Fund identifies several reasons for adopting different types of virtual money:
5020 $
bonus per i nuovi utenti!
ByBit offre condizioni comode e sicure per il trading di criptovalute, offre commissioni basse, un alto livello di liquidità e strumenti moderni per l'analisi del mercato. Supporta il trading a pronti e con leva finanziaria e aiuta i trader principianti e professionisti con un'interfaccia intuitiva e tutorial.
Guadagnate un bonus di 100 $
per i nuovi utenti!
Il più grande exchange di criptovalute dove è possibile iniziare in modo rapido e sicuro il proprio viaggio nel mondo delle criptovalute. La piattaforma offre centinaia di asset popolari, commissioni basse e strumenti avanzati per il trading e l'investimento. La facilità di registrazione, l'alta velocità delle transazioni e l'affidabile protezione dei fondi fanno di Binance un'ottima scelta per i trader di qualsiasi livello!
| Cheap transactions | VCBs are more cost-effective than cash because they have lower transaction costs |
| Access to financial products | Those who cannot use banking services will have easier and safer access to money |
| Restriction of illegal activities | CSECs can give private companies an incentive to comply with transparency standards |
| Developing financial relationships | Virtual currencies facilitate quick and smooth conduct of monetary policy |
There are also several challenges, each of which requires careful consideration before a country launches a CSEC:
- Citizens may withdraw large amounts of money from banks to buy the nation’s digital currency. This would result in an outflow of funds from financial institutions.
- Centralization through the government may cause negative reactions from users and create cybersecurity risks. Regulatory processes are not updated. To work with new forms of money, they need to be made more secure. Decentralized currencies use distributed ledgers, hence there is no central governance body. Blockchains maintain records of transaction activity and use consensus models to decide which transaction is genuine and which is not. Cryptocurrencies also use a number of algorithms and cryptographic techniques that provide security. The unresolved question is whether blockchain technology can be used for CSEC.
Central banks (CBs) are still in the early stages of exploring options for national digital money. According to the International Monetary Fund, the reason advanced economies may consider them is to counter the growth of private forms of virtual money.
A pilot project with a VCPB in China has forced major world powers to compete. The transition of technology from legacy forms to more advanced forms may allow the PRC to determine how the global payment infrastructure that facilitates the growth of cross-border trade and remittances will evolve.
Economists argue that CSECs have the potential to improve market functioning. The Bank for International Settlements said it could increase the flow of liquidity by speeding up operations. And the Central Bank of England said it can raise GDP by up to 3% by reducing transaction costs. In many emerging economies, CSEs are primarily seen as a means of increasing financial accessibility. Populations that cannot use traditional banking services are actively engaging in the digital economy.
Central banks control the circulation and supply of money around the world, but the phenomenal growth in the popularity of bitcoin and altcoins poses a threat to their authority, control and power.
List of existing state cryptocurrencies
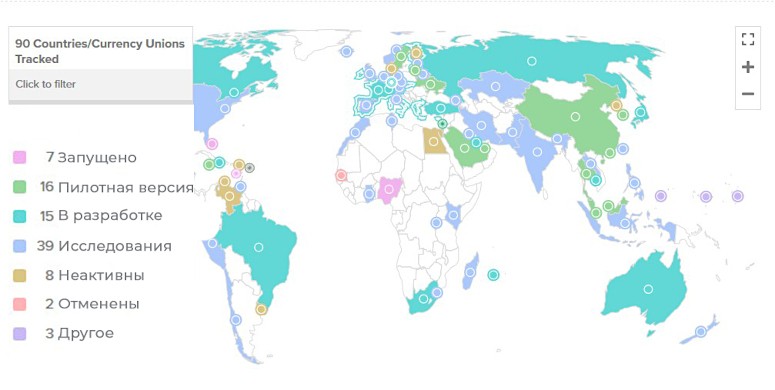
As of November 2021, 90 countries (representing more than 90 percent of global GDP) are exploring the use of their own VCs. Following the Eastern Caribbean conglomerate, the African continent has also shown interest in a state cryptocurrency. Another 14 countries, including China, Sweden and South Korea, are in pilot stages with their own central bank digital currencies. In total, 83 nations are in various stages of exploring the phenomenon of a national cryptocurrency.
As of November 2021, 7 countries have fully launched digital currencies: the Bahamas, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, Antigua and Barbuda, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, St. Lucia and Nigeria.
Despite all the benefits of digital currencies issued by banks, there are concerns that they could be used by governments to control their citizens.
Nigeria
This is the first African country to introduce a virtual currency. The digital money, dubbed e-Naira, is backed and issued by the Central Bank of Nigeria. The government believes that a national virtual currency is more cost-effective than physical cash. The CVCB helps people who do not have bank accounts to have easy access to money. Also, the objective of digital assets is to curb illegal activities in the country.
At the launch of e-Naira, 500 million coins worth $1.21 million were minted. So far, only bank account holders can access the nation’s cryptocurrency.
The next phase of implementation will include unbanked users. This category has reached 60 million consumers. Depending on the level of identification provided, a higher transaction limit for eNaira is allowed. With a phone number and a verified national identity, users can make payments of up to 50,000 digital naira ($121) per day.
Nigeria’s CSEC is officially recognized as a means of payment for goods and services.
Bahamas
In December 2019, the Central Bank of The Bahamas launched the Sand Dollar project. After successful testing, the virtual money was rolled out nationwide in October 2020. Sand Dollar is the world’s first nationwide digital currency issued by a central bank. The Central Bank is now working to achieve full interoperability between different wallet providers. Motivations for the CVCB pilot project included increasing accessibility to financial services and enhancing protection against money laundering or illegal economic activity.
Eastern Caribbean region
4 of the 8 member states have adopted the DCash digital currency: St. Kitts and Nevis, Grenada, Antigua and Barbuda, St. Lucia. The Eastern Caribbean Central Bank (ECCB) launched the coin in March 2021. The region became the first Central Bank in the monetary union to issue virtual money.

The project was realized, while solving such problems:
- High cost of banking services.
- Slow pace of trade development.
- Increased financial accessibility and the inability of banks to cover the needs of different segments of the population.
Buyers and sellers can use the DCash app. Its advantages:
- Fee-free transfers in real time.
- Reliable and secure DCash storage and transaction platform.
- Ability to send money instantly within the Eastern Caribbean Currency Union (ECCU).
- No minimum spending amount (as with some financial products).
- No bank account required.
- No minimum balance required for a DCash account.
- 24/7 access to transaction history.
- Confidentiality of transaction information.
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
The DCash virtual coin, launched for November 2021 in 4 of the 8 states of the Eastern Caribbean Currency Union (ECCU), is not yet available in St. Vincent and the Grenadines. Authorities say they will assess the feasibility of a full commercial launch for all eight member states of the conglomerate after 12 months.
Russia’s state cryptocurrency
The Central Bank of Russia plans to launch a pilot digital ruble platform in early 2022. The group of the first participants in the project will include 12 of the country’s largest financial organizations: Sberbank, VTB, Gazprombank, Alfa-Bank and others.
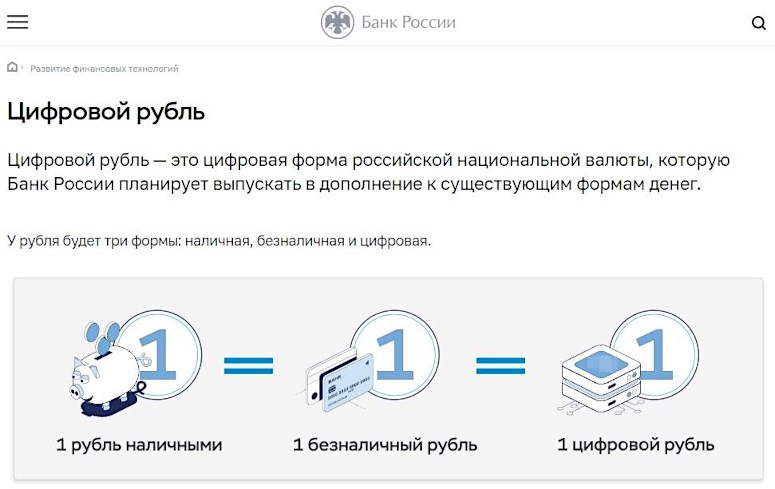
The Central Bank has set the goal of the pilot project to ensure a smooth transition from one form of money to another, so it wants to make sure that banks will be able to adapt their systems. The digital ruble will be a virtual form of national money, will have its properties and fulfill all functions.
Russia’s digital state cryptocurrency will be another form of money and will be in circulation alongside cash and non-cash rubles. All types of Russian money will be easily convertible into each other.

The introduction of a Russian virtual currency will require the creation of additional payment infrastructure. The Bank of Russia is also analyzing the possible effects of the alternative form of the ruble on price-setting policy and financial stability. Following public consultations, the Bank of Russia will consider the next steps in the implementation of the virtual currency project.
For 2022, the Central Bank has planned to test the prototype of the digital ruble platform and develop an implementation roadmap based on the results. This will be followed by adapting legislation to launch the state virtual currency.
According to Russian officials, modern technology will have a profound impact on monetary relations. New types of settlement units will appear. To prevent fragmentation of monetary systems and competition between private and public finance, banks need to develop appropriate regulation and infrastructure.
Financial organizations can create ecosystems around existing payment platforms and leverage the additional features of smart contracts.
Conclusions
Given the high potential costs and complexity of implementing a VCB, a legitimate question arises as to why many central banks are actively considering adopting a public virtual currency. The primary motivation is fear.
Many banks have expressed fears that bitcoin and altcoins will play a more important role in settlements. However, fears that cryptocurrencies will supplant or significantly reduce the influence of fiat money are exaggerated. Bitcoin and altcoins are unsuitable for the payments world, where stability of value is important. Central banks agree that coins and tokens do not fulfill the function of money:
- They are rarely used as a means of payment.
- They are not used as a unit of account.
- Their prices are unstable, so they are a poor means of saving.
Virtual assets are gaining popularity, their valuations are rising, and managers are creating funds to invest in them. But the same can be said for stocks or bonds. Governments are also seriously considering the development of stablecoins. It is believed that this type of crypto-asset could gradually replace national currencies, and central banks would lose control over monetary issues.
However, private steblecoins cannot serve as the basis for a sound financial system. They need strict regulation and supervision. Only then will steblecoins gain the trust of users. They need to build on the foundation provided by central banks to become part of the existing financial system.
Central banks of states have to take proactive steps to introduce national digital currencies. It makes sense to aim for cheap and fast virtual payments and greater transparency with users. However, the introduction of VCPPS takes time.
Privacy and security issues also remain unresolved. Central banks increase control over the issuance of money and gain insight into how people spend their capital. CSECs will only be useful if they are made open and transparent. And if central bank mechanisms are hacked, the entire virtual payment system could be fatally compromised.
Blockchain technology will help solve these problems. Such systems will provide a high level of security and anonymity. However, no central bank has yet used the blockchain mechanism to create a national cryptocurrency.
In the existing monetary relations, there are all the prerequisites for a transition to a low or zero cash economy based on the CBDC.
Frequently Asked Questions
🤔 Does China have a CSEC?
The PRC is in the pilot phase of a national virtual currency in 2021, but its main digital yuan system is centralized.
🙄 Is cryptocurrency legal in Russia?
As of January 1, 2021, digital assets are allowed in Russia, but they cannot be used as a means of payment.
❓ What is the blockchain underlying the digital currency?
No national digital currency uses distributed ledger technology. However, Ethereum can support the necessary requirements in terms of scalability and privacy.
🤷♂️ Are cryptocurrency and national digital currency the same thing?
A DNCB is different in that it has centralized governing bodies and it does not run on a blockchain.
💵 Is it possible to invest in a digital currency?
As long as national digital currencies are at the stage of pilot launches, it is not possible to invest in them. Big changes in finance and economics will be needed.
Is there a mistake in the text? Highlight it with your mouse and press Ctrl + Enter
Author: Saifedean Ammous, an expert in cryptocurrency economics.














