Distributed ledger technology has had a great impact on society. Blockchain revolutionized the financial industry by introducing cryptocurrencies based on decentralized control. The idea was to transfer the issuance of payment instruments from a single authority to society. Decentralization in blockchain then began to affect other sectors of the economy. Enthusiasts have proposed different methods of transferring control in current models of financial and social relationships. Many options are based on distributed data registries.
The general meaning of decentralization
Most often, businesses operate under a model in which decision-making authority is vested in the sole executive. For example, the CEO gives orders for important company processes.
Through decentralization, management functions are moved from one point to several.
This system allows the lower levels of the hierarchy to make decisions. The formats for transferring management functions are summarized in the table.
| Modell | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Decentralization of relationships | This is the use of blockchain to eliminate intermediaries. The parties transact through smart contracts. Decentralization eliminates the third party who owns the assets or data. In the business environment, you may hear about disintermediation. This is a phenomenon where 2 parties who used to rely on an intermediary to facilitate transactions transact directly with each other. Such a business concept is also described as peer-to-peer transaction (peer-to-peer). |
| Physical decentralization | This is the dispersal of servers in territories of different countries. When nodes are managed by strangers, it is impossible to interfere with the network or destroy data. The idea is to create a global infrastructure that is not owned by anyone. Everyone has the right to use this decentralized environment. For example, Bitcoin was designed to be uncensored. If a person owns BTC coins, no one can stop them from spending the cryptocurrency (provided they have internet access). Therefore, it is important for decentralized networks to have a large group of users to securely manage the nodes. Participants in the global chain confirm transactions in the blockchain and are rewarded for it. Running a single network of servers is physical decentralization. |
| Transactional decentralization | Blockchain technology has given the world a new model for making transactions. The network stores registries of transaction data in a secure way. Smart contracts automate business logic, securely accomplishing tasks. A harmonized data verification and validation process ensures the security and transparency of the network. |
Blockchain can be centralized and decentralized. In the first case, the network consists of participants whose identities are known. Only trusted nodes make entries in the ledger. The transactions of the participants can be verified. In a decentralized network, anyone is able to verify transactions.
For example, Bitcoin uses bányászat and proof-of-work to maintain the integrity of the ledger. Mechanisms are needed to deal with vulnerabilities to ensure that transactions are executed correctly.
5020 $
bónusz az új felhasználóknak!
A ByBit kényelmes és biztonságos feltételeket biztosít a kriptopénz kereskedéshez, alacsony jutalékokat, magas szintű likviditást és modern eszközöket kínál a piacelemzéshez. Támogatja az azonnali és a tőkeáttételes kereskedést, és intuitív felülettel és oktatóanyagokkal segíti a kezdőket és a profi kereskedőket.
Keress 100 $ bónuszt
új felhasználóknak!
A legnagyobb kriptotőzsde, ahol gyorsan és biztonságosan elindulhat a kriptovaluták világában. A platform több száz népszerű eszközt, alacsony jutalékokat és fejlett eszközöket kínál a kereskedéshez és befektetéshez. Az egyszerű regisztráció, a tranzakciók nagy sebessége és a pénzeszközök megbízható védelme teszi a Binance-t nagyszerű választássá bármilyen szintű kereskedők számára!
The impact of decentralization on people’s lives
The financial crisis of 2008 was not the only problem that humanity had to face. There have been many notable disruptions in various sectors that lacked centralization policies. Platforms (like Facebook or Airbnb) have become industry giants, able to dictate terms to their users. However, they are also vulnerable because of their centralized nature. Users of platforms are vulnerable to data manipulation or hacker attacks.
In parallel to these problems, the decentralized system on the blockchain slowly gained momentum. The first chains were ignored by the general public, but their potential has not gone completely unnoticed.
More and more projects are incorporating blockchain into their business (e.g. Walmart, Maersk, Nasdaq). Startups based on decentralized technologies are launched regularly (e.g. IDO on Solana, Binance Smart Chin, Ethereum). Blockchain offers broad solutions.
Reliability
Blockchain is considered secure because full copies of the registry are maintained by all active nodes. If one control point goes offline, the data is still available to all other participants in the network.
In a decentralized blockchain, there is no single point of failure.
The technology allows for unitary constructs that do not need an executive. The Internet has solved the problem of information sharing, while blockchain has made the transfer of value possible.
Átláthatóság
Most blockchains are open source software. Anyone can see how the software is written. Open source code allows auditors to check cryptocurrencies and other valuables for security. It also means there is no real power over who controls the code of digital assets and how it is edited. Anyone can suggest changes to the system. If the majority of the network’s users agree that the new version of the code is secure and worthy of consideration, then the blockchain is improved.
The decentralized network makes data open, which has not been the case in financial systems before. Many argue that the technology can be used as a new standard for transparency. Network participants access transaction information from shared addresses through a blockchain browser.
In the case of cybersecurity, this means that threat data can be open to the community. Transparency through blockchain eliminates any bias from companies that pay auditors to produce false reports.
Unboundedness
Blockchain has no dimensionality, so it is capable of storing an unlimited amount of information. When the network becomes too large, the nodes running a full client expand their hard disk space. The constant growth of the blockchain can be a problem in scalability.
Trans-boundary
Blockchain technology enables secure payments between an infinite number of bank registers. It bypasses middlemen when transferring money from one institution to another. Decentralization in blockchain solves these problems by storing each transaction in a secure distributed ledger. Once a transaction is registered, payment is available to the recipient without intermediaries, delays or fees.
Once a transaction is entered, it cannot be deleted or changed in the ledger. This increases transparency and security.
Advantages and disadvantages of decentralization
Distributed ledger technology has brought many benefits to different areas of the economy. A decentralized system in blockchain has the following advantages:
- Fraud prevention. Since blockchains are open source registries where every single transaction is recorded, it is easy to detect fraud. The integrity of the system is monitored and maintained by miners who verify transactions continuously. This makes decentralized structures virtually invulnerable.
- Protection from government interference. Blockchain-based cryptocurrencies are not controlled by the government, banks or central financial institutions. The state cannot interfere. A problem that often arises in traditional finance is inflation. Cryptocurrencies are programs with a fixed number of units of account. They are not subject to hyperinflation unlike national paper money.
- Acceleration of transactions. Bank transactions can sometimes take days to complete. However, blockchain transactions are most often confirmed in minutes. If money can be sent faster, then other assets are able to move at high speed. This is the basis for economic development.
- Increased financial activity. Decentralized networks allow transactions to take place directly between users without the involvement of a third party. Financial efficiency increases, people rely less on banks. Users save on fees and other costs associated with maintaining their accounts.
- Secure storage. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies can be kept in computers or mobile devices and sent online. People no longer need to buy safes or safe deposit boxes in banks to secure their savings.
All these advantages do not exclude the disadvantages of decentralized networks:
- An environment for criminal activity is created. The anonymous nature has made blockchains a popular tool among criminals. For example, the digital black market Silk Road relied on bitcoin transactions. On the site, people could buy illegal substances, weapons, and fake documents. All transactions were blockchain-based. Silk Road was shut down by the US Federal Bureau of Investigation. However, many still believe that decentralized technologies are too attractive for criminals and make it easier to finance illegal activities.
- Volatility. The prices of cryptocurrencies running on decentralized networks are often volatile. For example, the bitcoin exchange rate can rise or fall by thousands of dollars in a single day. The reason for this volatility is that cryptocurrencies are built on new technologies. Governments, investors, businesses and other users are trying to find solutions to control the volatility. So far, speculation has prioritized influence on digital asset rates. However, despite excessive volatility, the price of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is rising over time. Society is increasingly accepting and utilizing digital assets.
- Storage. Storing cryptocurrencies on decentralized networks can also be a challenge for people who are not tech-savvy. In theory, secure storage is relatively easy to achieve. For example, you can use Trezor and Ledger cold wallets. It would be difficult for the average person to create an account for bitcoin or etherium and move their digital assets from software storage to an offline device. Many cryptocurrency owners hold their capital directly on centralized exchanges. This is not safe. Exchanges are often targeted by hackers. The latter crack the program code and steal users’ assets.
The problem of decentralization in blockchain
The main sticking point with distributed networks will always be the loss of control and lack of coordination. The inability to reach an agreement when power is decentralized is called the problem of Byzantine generals. This situation can be summarized as a single question: how do you make sure that multiple decision makers at a distance are in absolute agreement on the actions to be taken? In other words, how do individual parties ensure that they have reached complete consensus?
For example, units of the Byzantine army are holding a besieged city. In order to strike, the generals of each division, scattered around the periphery of the fortress, must agree on a battle plan. While some commanders wish to attack, others decide to retreat.
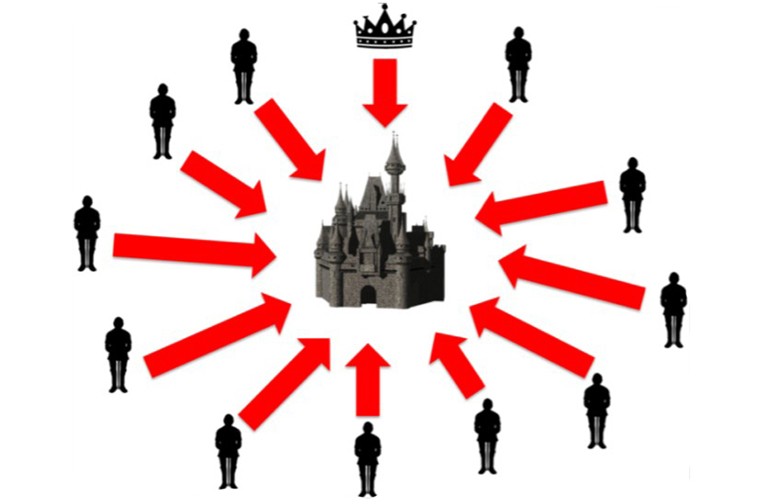
In the official description of the Byzantine generals’ problem (1982) proposed a leader-follower scheme. To reach consensus, the commanding general and each lieutenant must agree on the same solution. The situation is complicated by the fact that the principals are so far apart that they need messengers to relay messages. One or more lieutenants may be traitors seeking to sabotage the plan. Given these conditions, does the army implement the strategy?
The solution is based on an algorithm that ensures that:
- All loyal generals and lieutenants choose the same agreed-upon plan.
- Traitors cannot force loyal leaders to take the wrong action.
Loyal lieutenants will do what the algorithm dictates. Traitors can do whatever they want. The algorithm must guarantee the first condition regardless of what the unfaithful combatants do. Loyal lieutenants must not only come to an agreement, but agree on a reasonable plan.
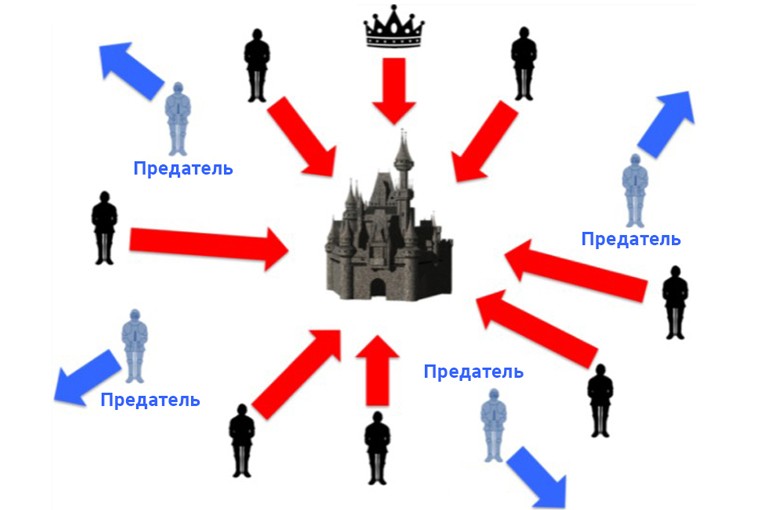
The problem of Byzantine generals is analogous to leaderless coordination between distrustful parties. The situation described is an example of how consensus is achieved in distributed ledger technologies (DLT), where all nodes are required to follow a set of rules to agree on a particular transaction before it is added to the database. This is not easy, especially in networks where there are thousands of participants. Everyone must agree on the validity of the incoming information in order to prevent sabotage by attackers.
The solution is a consensus algorithm where nodes work together to securely update the registry.
The future of technology
As decentralized registries become more prevalent, the way people live their lives is also changing. The following areas will be impacted by blockchain technology in the near future:
- Governments are likely to start adopting distributed ledgers to replace traditional systems. The transition to decentralized digital data storage will take some time. These solutions will provide trust and enhance security.
- Transparency between industries will increase. In the future, there may be a single blockchain that will be used by different companies and sectors. Having a common system will make business accessible to more stakeholders and provide transparency and security.
- States will shift from fiat money to cryptocurrency, as the latter is easier to track. Digital assets will be backed by physical values, and coin and token rates can be managed through various controls (e.g., issuing a large amount of money to lower the value of the dollar).
- The technology will solve identification problems. For now, systems operate in isolation and are prone to errors. Blockchain will provide a single source for identity and asset verification. Statistics show that nearly 1.5 billion people in developing countries do not have a proper means of verifying their data. An international identity platform on blockchain will offer non-citizens the ability to access legal documentation and the privileges that come with it.
- A decentralized network capable of regulating international economic relations. In 2023, it is an inefficient and dysfunctional process that slows down trade. Fraud, counterfeiting, political influence and errors are common. With blockchain, many of these problems will be eliminated. By harmonizing payment methods, paperwork and regulation into a single digital international system, much of the crime can be curbed. Distributed ledger technologies will build trust between countries and economic actors.
Decentralized Cryptocurrency Exchanges
In the digital asset market, a DEX is a peer-to-peer exchange, a code-driven exchange, a decentralized application (dApp) or a marketplace where people can trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
All transactions are done through intelligens szerződések.
Each transaction is recorded in the blockchain. There are 3 types of peer-to-peer trading platforms:
- Swap exchanges(AMMs or automated market makers). These platforms allow you to instantly exchange tokens with other users.
- DEX aggregators. With this technology, traders track orders from all decentralized exchanges in one place.
- Order book based exchanges. This type of DEX replicates the traditional trading model of centralized exchanges.
Among the large number of peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges, 5 platforms are leading the way:
- Uniswap. DEX on the Ethereum protocol charges a fixed transaction fee of 0.3%. Prices on the exchange are set using mathematical formulas, and trading takes place through smart contracts. The exchange has liquidity pools for this purpose.
- Bancor. The platform was the first to pave the way for DeFi apps. Bancor works differently than other DEXs. Transactions are made using its own liquidity pool, rather than being collected from buyers and sellers.
- Curve. This is a DEX designed for trading stablecoins. The platform is built on Ethereum. Curve charges low commissions, which ensures user loyalty.
- PancakeSwap. A popular DeFi protocol that runs on the BSC (Binance Smart Chain). Also utilizes liquidity pools. PancakeSwap rewards investors who delegate CAKE tokens they own to the platform.
- SushiSwap. This is a popular decentralized exchange based on Ethereum, where you can exchange tokens, get rewarded by growing crops. The platform was created on the basis of the leading DEX Uniswap. It initially derived liquidity through a process called “vampire mining”.
Összefoglaló
Applications built on blockchain technology go far beyond financial or business solutions. It is reasonable to expect that the initial wave of interest and investment from these sectors will provide greater impetus for development. Borderless value exchange and accessible digital identities have the potential to empower people who do not participate in the global financial system.
Decentralized repositories of large data sets will increase the security of any entity’s operations because there is no control by a single owner. However, how distributed should the network be? After all, humanity still does not know what level of decentralization is safe.
Gyakran ismételt kérdések
❗ Why is decentralization important for blockchain?
The point is to create an immutable and open data registry.
✅ Which blockchain came first?
Bitcoin is the progenitor of decentralized networks.
❔ What are dApps?
Decentralized applications are software codes that run and store data based on the blockchain rather than on a single computer.
❓ Which cryptocurrencies are decentralized?
All coins and tokens in circulation. are based on public blockchains and are not subject to a single governing body.
❕ Is the Internet a decentralized network?
Most platforms are at the mercy of corporations. However, in 2020-2021, a trend has emerged to create a decentralized internet. The network will operate without the involvement of operators.
Hiba van a szövegben? Jelölje ki az egérrel, és nyomja meg a Ctrl + Lépjen be.
Szerző: Saifedean Ammous, a kriptovaluta közgazdaságtan szakértője.















