Blockchain is a database containing information about all cryptocurrency transactions of the system participants. In fact, the term is used as the name of the technology of building data on transactions in the network. Validators in the blockchain are engaged in confirming such transfers. A lot of people are confused with this concept.
Who is a blockchain validator?
This term refers to a validation node. Its main tasks are to compare the received information with the existing information and confirm the block of the chain. That is, adding it to the network. This can be done without the large computing power that is required in Bergbau.
The absence of validators will cause the blockchain to fail. However, the interest in becoming validation nodes is fueled by issuing rewards for proper functioning. Therefore, the blockchain will never stop.
Usually, verification nodes are automatically selected for each blockchain based on the principle of randomness. However, several things have an impact:
- The age of the stake (the period of smooth operation of the node).
- The state of the node (from Latin nodus – node).
- The number of blocked cryptocurrency.
Nodes with a large number of coins have an advantage. However, outages will result in penalties.
5020 $
Bonus für neue Nutzer!
ByBit bietet bequeme und sichere Bedingungen für den Handel mit Kryptowährungen, niedrige Kommissionen, hohe Liquidität und moderne Tools für die Marktanalyse. Es unterstützt den Spot- und Leveraged-Handel und hilft Anfängern und professionellen Händlern mit einer intuitiven Schnittstelle und Tutorials.
Verdienen Sie einen 100 $-Bonus
für neue Benutzer!
Die größte Kryptobörse, wo Sie schnell und sicher Ihre Reise in die Welt der Kryptowährungen beginnen können. Die Plattform bietet Hunderte von beliebten Vermögenswerten, niedrige Kommissionen und fortschrittliche Tools für den Handel und Investitionen. Die einfache Registrierung, die hohe Geschwindigkeit der Transaktionen und der zuverlässige Schutz der Gelder machen Binance zu einer guten Wahl für Trader jeder Ebene!
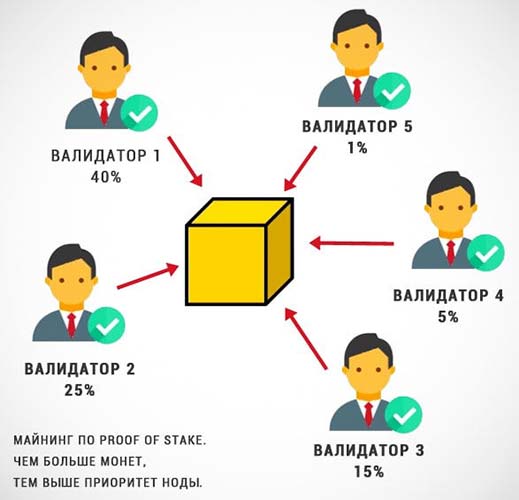
Technically, you should not compare a validator with a miner. Although the former also obtains cryptocurrency, but using a different algorithm. The mining nodes appear to be a subset of the validation nodes.
In the algorithm, proof-of-work is actively used by miners. However, they are not provided in Proof-of-Stake (PoS) for lack of necessity.
Why steaking is needed
PoS (Proof-of-Stake) incorporates the basic principle of capitalism – money must work. A validator buys a set number of coins or more. Next, freezes them in a personal wallet. From that point on, the person becomes a trustee of the system.
Staking increases the security of the blockchain’s operation. After all, large computing power is not needed. Attacks on the network become unprofitable because of the need to invest large amounts of money. Cryptocurrency is mined only after freezing assets in the system and setting up nodes.
Staking has 3 advantages:
- The speed of block verification is increased.
- Network defense costs are reduced.
- Deposit and withdrawal fees are reduced.
It turns out that Proof-of-Stake is beneficial to 3 parties: validators, companies issuing coins based on this consensus algorithm, and traders (investors).
However, PoS has some negative aspects as well:
- High entry threshold due to the need to buy a set number of coins. With a small budget, it is better to consider startups that are just rolling out the network.
- Not every coin is characterized by high returns on staking.
- Young organizations are at risk of capturing a large share of trusted validation nodes. This is due to the low capitalization of the coin. It is easier for attackers to seize 51% of the hashrate of their network.
Reward
Miners for holding a certain number of coins are rewarded with new coins. This approach keeps the blockchain system balanced. There are always enough validators. The network is kept secure.
The amount of transaction validation payments depends on the number of coins frozen. For example, a node possesses 3% of the total amount of coins among the nodes. Then it claims a corresponding portion of the profits.
Validators and Ethereum 2.0

The official launch of the first phase of Ethereum 2.0 is December 1, 2020. The deposit contract of the system had 524,288 ETH in the Beacon Chain. This is called a beacon chain. Anyone can become a verification node.
Since there are too many ideas in Ethereum 2.0, the implementation is still ongoing. Here is a brief summary of the main innovations from the project roadmap.
| Phase | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| Launch of Ethereum 2.0 project and realization of Beacon Chain with a minimal set of basic features | Splitting the system into shards – segments. This will allow to conduct parallel operations in the network and accelerate their processing. At first 64 shards with scalability will be realized | The phase is not specified in the roadmap. Vitalik Buterin proposed to use the new ETH 2.0 much earlier. For this purpose, it is planned to move ETH 1.0 to 2.0 after the first phase, but to do it before the second phase starts | Combining all the functions of the system. Re-implementation of smart contracts. Equipping the eWASM shards as EVM 2.0 (virtual machine) |
Participating in steaking
To start mining cryptocurrency, you need to freeze a minimum deposit of 32 etheriums on your wallet. As of September 12, 2021, this amount is approximately equal to $110,000. Ethereum 2.0 uses the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm. No computing power is required.
The amount of the reward depends on the number of blocked coins. The project management reported the maximum possible annual profitability of the validator – up to 20%. In reality, the profit parameter is about 2-5% due to the large number of validation nodes.
The network does not allow withdrawal of frozen funds until the launch of phase 1.5. It will mark the addition of dynamic blocking (27 hours / 256 epochs – Beacon Chain links). The goal is to prevent investors’ funds from leaking out of the system.
Self-stacking
Noda check can become one on its own. To do this, you need to make a deposit of 32 ETH. And freeze the specified amount on the wallet. The funds will be blocked until phase 1.5. It is also necessary to comply with the technical requirements when starting the blockchain verification process.
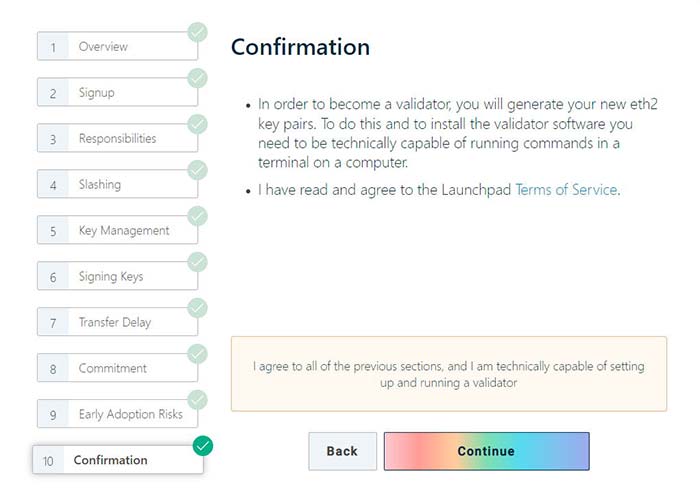
To become a validator, you should use the instructions on the official website of the project ethereum.org. The guide contains 3 steps:
- Accept the terms of processing and validating transactions within the network, also participation in the signal chain. It is mandatory to read the 9 provisions and confirm awareness of the risks.
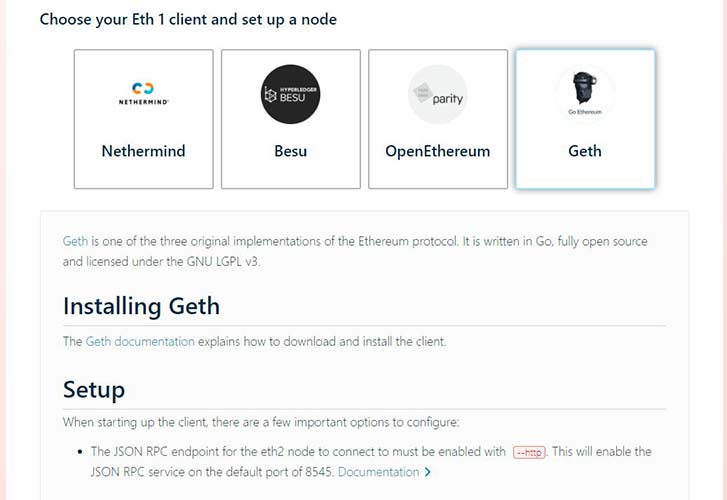
- Run Ethereum 1.0 and 2.0 clients in parallel. Choose software version 1.0. Follow the installation guide on the website. This will allow you to set up automatic processing of incoming verification node deposits from the ETH 1.0 network. Then select version 2.0 software and follow the instructions on the website. This will ensure that the node will be programmed to work.
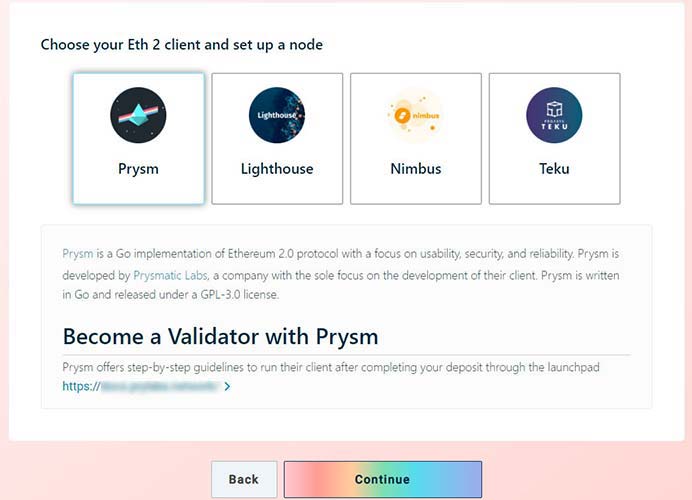
- Enter 32 etherium. It is mandatory to follow the manual in order to preserve the investment. Deviations of actions from the instructions can lead to the loss of capital. The transfer is made to the specified smart contract address.
Starting the verification node on your own is complicated. Difficulties can be avoided by using pre-configured equipment. For example, through Avado or Launchnodes services. To keep it running, receive a reward for validation and manage etherium coins will be a middleman for a fee.
In this case, to raise a node, the user will need to make a deposit of 32 ETH and additionally pay for equipment rental.
Another option is to cooperate with organizations that implement the concept of “validator as a service”. The service will manage the node for a small fee. The solution will suit institutional and simply large investors. Examples: Blox Staking, Stakewise Solom, Attestant.
Collaborative Staking
A large deposit of 32 etherium (₽8,039,000 as of September 12, 2021) is required. This determines a high threshold of entry. Only a secured investor can become a validation node. The solution to the problem is co-stacking. It is available through special services.
Ethereum 2.0 developers posted a post with a list of such resources. However, the leaders of the project state that it is necessary to independently verify the risks when using the services of these organizations. They have not undergone an official examination.
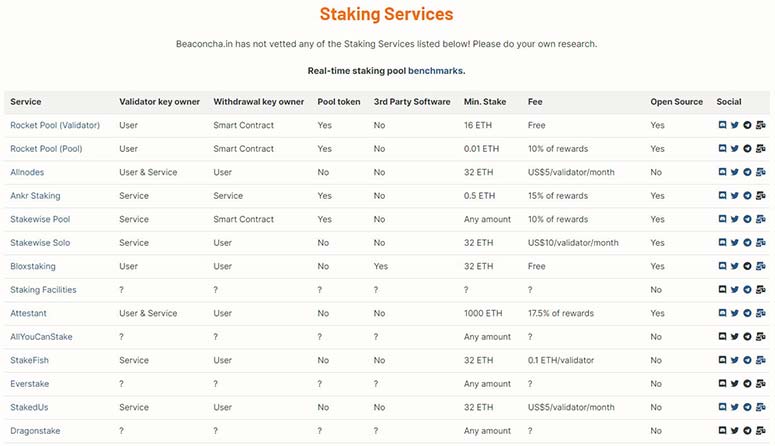
Objectively, there are 3 ways to participate in co-stacking:
- Pools. Are intermediaries between people and crypto networks. Combine the funds of several investors into a deposit and freeze them on the wallet of the organization. The share of the investment determines the amount of profit from the total income. Cryptocurrency is stored in a decentralized manner. Information is available to each pool participant.
- Lending platforms. Allow maximizing the profit from staking by issuing loans to freeze ETH in the system.
- Exchanges and custodians. Present themselves as the simplest way to participate in co-staking. The principle of functioning is almost completely similar to pools. Withdrawal of any funds is prohibited for a set period of time. The user does not take control of private keys.
Schlussfolgerung
Validator in the blockchain is a node of the system that checks and confirms incoming transactions of the network. It appears to be the main element of the chain. Without node validation, it is impossible for a crypto network to function.
It is technically incorrect to compare validators and miners. They perform different functions and work together in the same direction. Both groups are rewarded with cryptocurrency.
Staking makes it much easier to mine coins and increases the security of the blockchain. Attacks on networks that use the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm become unfavorable. However, steaking requires a large investment.
Ethereum 2.0 is a prime example. The threshold of entry as of September 12, 2021 is over $110,000. Nevertheless, the problem is being solved through co-staking or lending platforms.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
❓ Is a 51% attack on crypto networks with a Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm possible?
Possible. But it becomes less resource-intensive in terms of equivalent computing power. An attacker would need large reserves of cryptocurrency. Though sharding makes this task easier.
❌ What is the danger of a 51% attack?
The attacker gets the opportunity to create an infinite number of forks. The classic defense method is to prohibit branching below a specified depth.
❔ Why are attacks on Proof-of-Stake networks unprofitable?
The PoS consensus algorithm requires a huge investment. This does not equate to a modest profit.
❕ Are there limits to the number of active validators?
Only the minimum number of active validation nodes is 16,384. That is how many were needed to run Beacon Chain.
❗ Is it safe to freeze 32 ETH for steaking in Beacon Chain?
The Ethereum 2.0 code is still considered to be new. However, the developers guarantee that there are no vulnerability issues.
Befindet sich ein Fehler im Text? Markieren Sie ihn mit Ihrer Maus und drücken Sie Strg + Eingabe
Autor: Saifedaner Ammouseinem Experten für die Wirtschaft der Kryptowährungen.















