Trading platforms act as intermediaries in the procedure of buying and selling digital assets. Orders on a cryptocurrency exchange are exchange bids that users send to the server. Such offers do not always provide for instant conversion of one asset into another. In some cases, the order is executed after a long time or is automatically deleted altogether. Beginners need to understand the types of trade orders in order not to make a mistake when exchanging digital money.
The concept of an order on a cryptocurrency exchange
Most trading platforms operate in a centralized manner. A crypto exchange has a single server that collects and stores user bids. The registry is called an order book or orderbook. Transaction processing is also centralized:
- Customers make a deposit (fiat or digital money). The funds are transferred to a single exchange liquidity pool.
- The buyer orders a certain amount of cryptoassets at a selected rate. This can be either the current market price or the price expected in the future.
- The second party to the transaction makes a counteroffer. If the conditions of both participants coincide, the server processes the transaction.
Of key importance in this process is the order – a client’s instruction to buy or sell a cryptoasset. This order specifies the direction of the exchange, the execution price of the transaction and its volume.
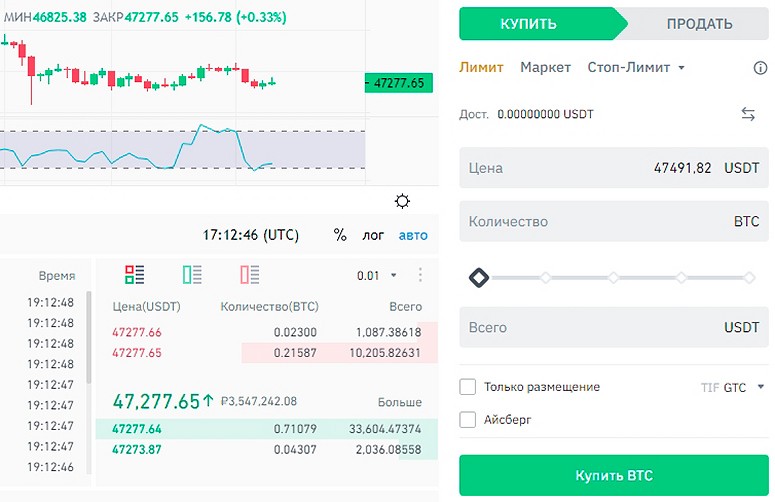
Types of orders on the cryptocurrency exchange
In different types of orders, the execution procedure differs. In one case, the operation is completed immediately at the current rate, in others – it is postponed until certain conditions are met. These can be:
- Reaching the quotes of the level set by the trader.
- Correction of the cryptoasset rate after a pronounced trend movement.
- Gradual change in the price of symboler and coins in the desired direction for the user.
The terms of the order can provide for its deactivation after some time. This protects traders from triggering outdated orders if the situation on the cryptocurrency market has changed.
5020 $
Bonus til nye brugere!
ByBit giver bekvemme og sikre betingelser for handel med kryptovaluta, tilbyder lave provisioner, højt likviditetsniveau og moderne værktøjer til markedsanalyse. Den understøtter spot- og gearet handel og hjælper begyndere og professionelle handlere med en intuitiv grænseflade og vejledninger.
Optjen en 100 $-bonus
for nye brugere!
Den største kryptobørs, hvor du hurtigt og sikkert kan starte din rejse i kryptovalutaernes verden. Platformen tilbyder hundredvis af populære aktiver, lave provisioner og avancerede værktøjer til handel og investering. Nem registrering, høj transaktionshastighed og pålidelig beskyttelse af midler gør Binance til et godt valg for handlere på alle niveauer!
Marketplace
On English-speaking crypto platforms, it is usually signed as Market Order. It is executed at the best price available in the orderbook.
Beginning traders should keep in mind that the transaction is not always processed instantly. The exchange speed depends on the server response time to requests and liquidity (availability of assets on the exchange’s balance sheet). Therefore, in some situations, the transaction is rejected or carried out at a new price.

Limit
On some crypto exchanges is called as Buy/Sell Limit. The transaction is processed if the rate of the asset reaches the level calculated by the user. Limit transactions are executed at a price that is more favorable to the party than the current market rate.
For example, if at the moment of sending an order of the Buy Limit type, the cryptocurrency quotes reached the $1000 mark, the order form can specify the activation price in the range of $1-$999.
By default, the order remains valid until it is triggered or canceled by the user. Experienced traders try to deactivate such orders as soon as the market situation changes.
Stop Loss
Can be called Stop Loss. Some platforms also use the term “market stop”. Its purpose is to fix losses if the cryptocurrency rate changes in the opposite direction from the desired one. For example, if a trader buys an asset at a price of $1000, he must take into account a possible error in the analysis and the risk of collapse of quotes. By setting the stop loss value at $900, the user instructs the crypto exchange to exchange the held assets as soon as the rate decreases to this level.
Skilled traders always trade by setting a Stop Loss. This protects them from losing their deposit. But placing an order in the order book does not guarantee its execution at the specified price. If there is panic in the market, quotes can change too quickly. The transaction will be processed at a less favorable rate.
A market stop can be used not only to fix losses. In some strategies, opening a position is allowed only when there is a pronounced trend movement. In this case, a market stop allows you to buy an asset only if it goes up in price and the quotes reach an important price level.
Scalable
This type of order is designed for a gradual accumulation of a position. On English-language platforms, it is usually signed as a Scalable Order. Since no trader can predict in advance the exact movement of quotes, many trading strategies provide for the gradual purchase of assets. In this case, clients specify in the order form at what interval on the chart the repeated transactions should take place. Usually, each stage of the transaction is tied to the price of the crypto-asset, calculated in pips or dollars.
Time in Force
The situation on the cryptocurrency market is changing rapidly. Intense growth of quotes can turn into a sharp decline in a few hours. In such conditions, traders’ forecasts are immediately outdated.
To protect against erroneous trades, Time in Force (TiF) orders are used. Usually the date and time of execution are specified in the order-form. If there are no exchange conditions in the market by that time, the transaction is canceled.
Passive
On many crypto exchanges, the terms “taker” and “maker” are found. Into such categories, the platform divides traders depending on how they affect the liquidity of the site.
| Trading style | Taker | Maker |
|---|---|---|
| Order of participation in transactions | Places orders of the Market type. Makes trades with users who have already placed a bid in the order book. | Adds its own exchange bids to the book |
| Effect on liquidity | Reduces the amount of assets available for exchange | Increases the liquidity of the crypto platform |
| Level of commission charged to the trader | High. The difference with the maker’s commission can reach 0.1-0.2%. | Low. In some cases, the fees are set at zero or provide for the accrual of a small reward to the client. |
It is profitable for the user to trade as a maker. This reduces the rates of commissions. Passive orders stipulate that the transaction will be carried out only if the trader acts as a maker. In the opposite case, the order remains in the orderbook or is deactivated. On English-speaking platforms such operations are called Post Only.
Order formation procedure
To create a new order on most crypto exchanges, you need to perform the following actions:
- Authorize on the platform and go to the trading terminal.
- Choose a direction.
- Specify what type of order on the cryptocurrency exchange (market, limit, stop-loss) the trader wants to use.
- If the exchange is not planned to be executed immediately, you should enter the conditions for buying or selling assets.
- Specify the transaction volume.
- Press the order activation button (can be signed as Buy, Sell or “Confirm”).
Ofte stillede spørgsmål
✅ Which orders are better to use for beginners?
It depends on the strategy. It can be difficult for beginner traders to predict in advance at what levels a trend change will occur. Therefore, it is better to open trades at the current market price.
❓ Do all exchanges have the same list of available orders?
No, in some cases you can only buy crypto-assets at the current rate. If the platform description does not specify the types of transactions, you should contact support.
🔎 How can I view the orderbook?
Most platforms have a corresponding column in the terminal. Only instant cryptocurrency exchange services are an exception, in which the interface is simplified.
💻 Is information about transactions on exchanges entered into the blockchain?
No, all information is processed on the crypto platform server.
💡 What is the difference between order execution on decentralized exchanges?
There is no orderbook on such platforms. Instead, liquidity pools are created in its place. A decentralized exchange does not store clients’ money, but ensures the transfer of assets between traders’ wallets.
Fejl i teksten? Fremhæv den med musen, og tryk på Ctrl + Kom ind.
Forfatter: Saifedean Ammousen ekspert i kryptovaluta-økonomi.