The first digital asset Bitcoin appeared in 2009. Its developer is considered to be Satoshi Nakamoto. In 8 years, by 2017, the number of users had increased significantly, and the load on the network became critical. Commissions for transactions went up, and the waiting time for their confirmation increased several times. To solve this problem, in May 2017, a council of the largest miners was organized, at that time controlling 80% of the network. During it, it was decided to do a protocol hardfork, and Bitcoin split into Bitcoin Cash (BCH) and classic Bitcoin. The split occurred due to the reluctance of the majority of the community to make drastic changes to the protocol. As a result, 2 irreversible blockchains were formed.
What is a cryptocurrency split
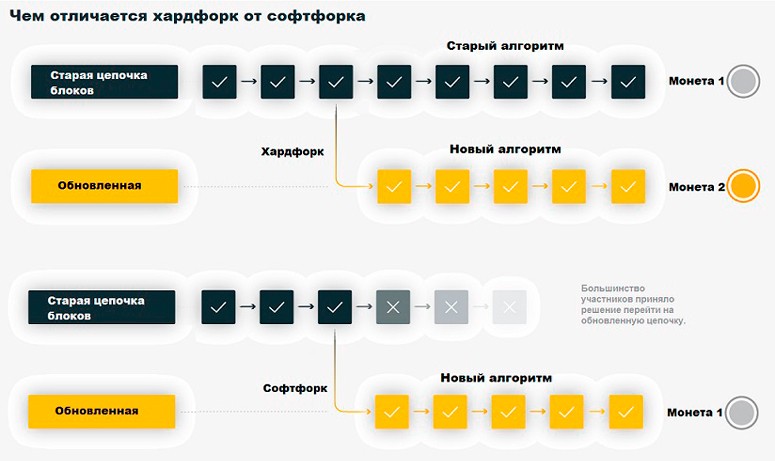
Algorithm updates are made to address technical issues that arise during the course of the system. Many digital currencies do not have a central governing body. In order to make global changes, an absolute majority vote of the community is required. If no compromise can be reached, then there may be a branching of the existing blockchain into 2 chains operating under different rules. This is what happened when BTC split into two cryptocurrencies. A group of miners who supported these changes switched to mining coins in the new network, while the majority remained to support the classic system.
Types of cryptocurrency forks
Each new block contains part of the information of the previous one, due to which the immutability of data and the integrity of the entire system are achieved. The general consensus accepts the longest chain as true, and the shorter chain “dies out”. However, due to scalability issues, changes in protocol operation may be allowed:
| Update Type | Popis |
|---|---|
| Softfork | Technology upgrade without the need to change software. New blocks are validated and included in the shared registry. |
| Hardfork | Splitting the blockchain into 2 branches due to a global update of the protocol. Some participants for various reasons do not want to accept the new rules and continue to work according to the old scheme. This leads to the fact that subsequent blocks cannot be confirmed by all nodes. Two circuits begin to exist in parallel, losing compatibility between them. |
Reasons for Bitcoin’s split
The laid algorithm in the network of the first cryptocurrency sets the time of finding a new block at the level of 10 minutes, and its size is 1 megabyte. As the number of transactions increases, there is a queue for data processing and fees increase. The transaction of the user who will pay more for the cryptocurrency transfer will be included in the register first.
To overcome the network load and increase the speed of transactions, a group of miners suggested raising the block size limit from 1 to 8 MB. However, not everyone agreed with such a radical change due to the loss of compatibility with previous chains and the emergence of the need for software updates.
There were also fears that the organizers might start těžba on the new protocol before the others and take over a large part of the network. Because of these disagreements, the Bitcoin split occurred.
5020 $
bonus pro nové uživatele!
ByBit poskytuje pohodlné a bezpečné podmínky pro obchodování s kryptoměnami, nabízí nízké poplatky, vysokou úroveň likvidity a moderní nástroje pro analýzu trhu. Podporuje spotové i pákové obchodování a pomáhá začátečníkům i profesionálním obchodníkům díky intuitivnímu rozhraní a výukovým lekcím.
Získejte bonus 100 $
pro nové uživatele!
Největší kryptoměnová burza, kde můžete rychle a bezpečně začít svou cestu světem kryptoměn. Platforma nabízí stovky oblíbených aktiv, nízké poplatky a pokročilé nástroje pro obchodování a investování. Díky snadné registraci, vysoké rychlosti transakcí a spolehlivé ochraně finančních prostředků je Binance skvělou volbou pro obchodníky na jakékoli úrovni!
History of forks in the Bitcoin network
The need to update the code came in 2011, which led to the BIP standard. Any participant can propose improvements to the algorithm, having first made sure that they will not harm the security and stability of the system.
There are 3 types of BIP:
- Informational. Do not propose any changes to the algorithm.
- Procedural. Describe proposals to make updates to the codebase and establish a process for doing so. Defines a path for future development of the project.
- Standard. A list of enhancements aimed at changing the code base.
The following steps must be completed for an update to take effect:
- Project. The generated idea is posted on the open GitHub repository for participants to evaluate the need for changes, raise objections, or leave recommendations.
- Proposal. An implementation scheme and criteria for inclusion in the physical blockchain are developed.
- Final adoption. The process of finalizing an idea goes through a voting stage. In the case of softfork, 95% of the nodes in the network need to approve.
The ease with which a new blockchain can be made generates variations based on the same basic concept but different from the original. In these situations, the blockchain undergoes a process known as branching.
Dozens of hardforks have been carried out since the Bitcoin network emerged, but only a few have become popular projects:
| Název | Popis |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin XT. | Was aimed at increasing throughput to 24 transactions per second. To this end, it was proposed to increase the block size to 8 MB. After several months, the project was still unable to gain community support. |
| Bitcoin Classic | In early 2016, some miners proposed to scale the blockchain by increasing the bandwidth by 2 times. However, 3 months after Bitcoin Cash separated from the network, support for the protocol was closed. |
| SegWhit | Changes to the data storage structure, transaction confirmation mechanism, and increasing the block size to 2MB were planned. The proposals were accepted by the softfork procedure on August 24, 2017, receiving approval from more than 95% of the network participants. |
| Bitcoin Unlimited | The idea of removing the 1MB limit was proposed, which could increase the profitability of mining by increasing the collected commissions in the blockchain. Developers opposed due to fears of centralization. If the limit were to be eliminated, the equipment requirements would significantly increase, and small miners would switch to other digital currencies. |
Bitcoin Cash
The first cryptocurrency was created as a peer-to-peer payment network for use in everyday transactions. Over the years, as it became popular and the price skyrocketed, bitcoin became an investment tool rather than a means of payment. The blockchain had a scalability problem as it could not handle the increased number of transactions. Confirmation times and fees for transfers on the blockchain increased dramatically.
Bitcoin Cash was launched on August 1, 2017, increasing the block size to 8MB, allowing more transfers to be processed. The project otherwise used the same source code with an issue limit of 21 million coins and a Proof-of-Work consensus method. The non-acceptance of this update by the majority of participants led to Bitcoin splitting into two cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin Gold
In October 2017, the second split happened, which resulted in another chain being separated from the original blockchain. It was aimed at breaking the monopoly of large miners using hardware (ASIC) that is unavailable to most users. For this purpose, the algorithm was replaced by Equihash, allowing for cost-effective mining of cryptocurrency on video cards and thus ensuring the decentralization of the network. At the time of the hardfork, Bitcoin owners received BTG at a 1:1 ratio for free. All information up to block 491,407 has been moved to the new branch. Capitalization as of mid-November 2021 is $1.1 billion.
Bitcoin SV.
The cryptocurrency emerged on November 15, 2018, due to a disagreement over changes to the VSN protocol. The splinter group refused to accept the updates:
- Canonical Transaction Ordering (CTOR). Another process for writing data to blocks.
- Check data SIG. Transaction code enables the powerful concept of an “oracle” – object that integrates offline data into the blockchain. There is an emerging opportunity to leverage inteligentní smlouvy.
This led to a split into Bitcoin SV and ABC. The first group of developers decided to follow the canonical principles of Bitcoin, only increasing the block size, the second team supported the modified protocol. Until now, there is still an open feud between them and accusations of trying to hack each other’s projects.
Follow-up
Making a Bitcoin fork is not difficult, the code is in the public domain. Often the coins after the split do not differ from the original in anything but name and are of no use. There are also projects when the cryptocurrency split, but was not accepted by the community and did not become a popular means of payment:
- Bitcoin Private. Uses a high privacy blockchain where transaction information is available in a public registry, but without a sender or recipient. Market capitalization: $16 million as of November 2021.
- Bitcoin Diamond. Employs an 8-megabyte blockchain and replay protection. Utilized Lightinig Network technology to significantly increase throughput and reduce fees. Capitalization as of November 2021: $375 million.
- Bitcoin God. Launched on December 27, 2017. Had innovations in the form of smart contracts and increased block size. The project is now closed.
Často kladené otázky
❓ What is consensus?
In a decentralized network, copies of blockchain records are stored on multiple nodes. By constantly mining new blocks and displaying this data in a registry, there is an algorithm by which participants come to an agreement on which variant to consider valid.
📅 How do I know the dates of the hardfork?
When the algorithm is updated, the information is published on the developers’ communication channels with the community (official website, social networks and others).
❕ What happens to the blockchain from which the new chain has disconnected?
It continues to operate as before while the nodes are mining blocks.
✅ Do forks happen in other cryptocurrencies?
Changing how the algorithm works is a necessary part of the existence of any major digital currency. It allows the project to scale to meet the needs of the community and the market. For example, Ethereum is planning a global protocol upgrade and a switch to version 2 to replace the network’s consensus method (energy-consuming Proof-of-Work with Proof-of-Stake).
⏳ Why is transaction confirmation time not decreasing as the number of miners grows?
Bitcoin’s code base has a principle: a new block should be in in 10 minutes. When the computing power of the network increases, the complexity of the cryptographic tasks performed is artificially increased so that the generation time remains unchanged.
Is there an error in the text? Highlight it with mouse and press Ctrl + Vstupte na
Autor: Mgr: Saifedean Ammous, odborník na ekonomiku kryptoměn.














