Distributed ledger technology, like the steam engine and the Internet, has sparked a revolution in economic and business models. The ability of decentralized networks to provide disintermediation, transparency and verifiability reduces transaction costs, improves the efficiency of existing supply chains and opens up new markets. The advantages and disadvantages of blockchain make the technology applicable in a variety of ways. While blockchain was developed in 2009 to create a payment system free of banks and governments, 12 years later hundreds of industries have adopted distributed ledgers to simplify business processes.
What is blockchain technology
A blockchain is a public digital ledger that stores all transactions in chronological order. Each block consists of information about thousands of transactions. Computers called nodes verify transactions by solving math problems. When a transaction is validated, the block is attached to the next element in the chain. This happens over and over again.
Blockchain technology is also based on a peer-to-peer network and is provided by millions of computers, so it is publicly available and transparent. This means that a third party cannot control the blockchain.
The information on the distributed ledger is available to anyone at any time.
Principle of operation
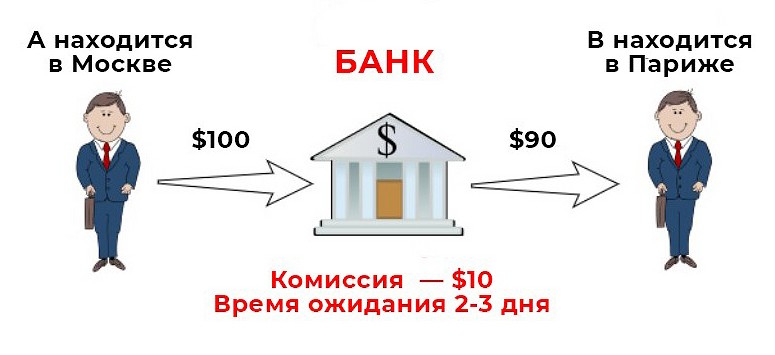
Here is the algorithm of an ordinary banking transaction: 4 people – A, B, C and D – would like to send money to each other. In the classical model, each of them will have a bank account. The financial organization will check if the client has enough money to complete the transaction.
If A wants to send $100 to user B, the procedure will look like this:
5020 $
bonus for new users!
ByBit provides convenient and safe conditions for cryptocurrency trading, offers low commissions, high level of liquidity and modern tools for market analysis. It supports spot and leveraged trading, and helps beginners and professional traders with an intuitive interface and tutorials.
Earn a 100 $ bonus
for new users!
The largest crypto exchange where you can quickly and safely start your journey in the world of cryptocurrencies. The platform offers hundreds of popular assets, low commissions and advanced tools for trading and investing. Easy registration, high speed of transactions and reliable protection of funds make Binance a great choice for traders of any level!
- The bank will check to see if A has money in his balance.
- $100 will be debited from A’s account.
- It will be transferred to B’s bank account.
The procedure requires time and bank fees.
Now we can consider how the scenario is realized through the blockchain. There is no longer a central governing body. Customers A, B, C and D are in direct contact with each other as if they were sitting at the same table. If the participants met physically, they could transfer money directly. But because they are in different countries, new conditions arise.
Uniqueness
Blockchain is the technology behind digital assets. It is an immutable ledger responsible for recording economic transactions that can be programmed to keep financial transactions and records of anything of value. A decentralized network is not controlled by a third party or financial institution. Distributed ledgers are built on certain principles.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Each participant in the transaction can see who sent and received money, how much money was transferred. |
| Openness | Information is available for everyone to check at any time. |
| Speed | Transactions are performed directly between participants, there is no third party that can delay the execution of the operation. |
| Low costs | There is no intermediary who needs to be paid extra. The cost of the transaction is reduced. |
| Security | Every transaction becomes publicly available. This leaves no room for fraud. |
The main advantages of blockchain
Distributed ledger technology is a database that is not hosted on a server owned by a company, but on a network of many computers. You can add new information to the blockchain, but you cannot change the information that is already stored there. The network constantly checks the authenticity of the database. The advantages of blockchain include the following.
Data protection
The registry is designed to keep track of all transactions on the network. Once money has changed hands, someone has to document the process. On the blockchain, each participant marks transactions as they occur and records information about them:
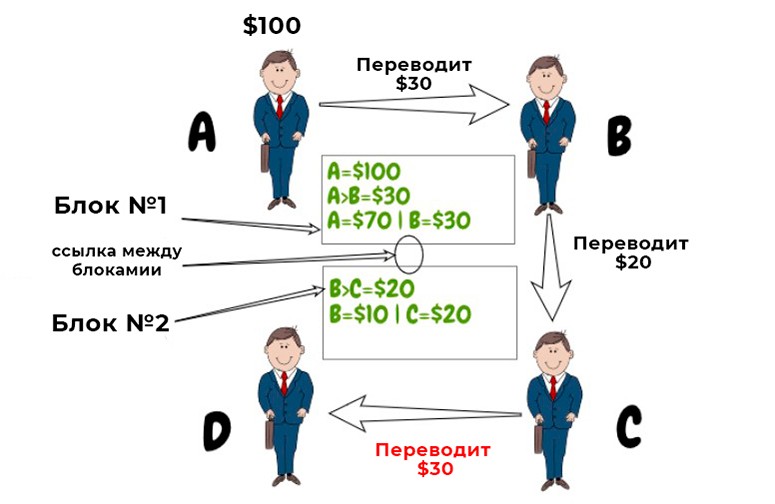
- Users A, B, C, and D record the transactions in a register. Then they check to see if the information is correct.
- If A transfers $100 to B, a transaction is created. Each person can view the information about it. If the transaction goes through, the network members enter it into the register.
Now it can be seen that B owns $30 and A’s account has decreased by $30. This information can be verified.
B transfers $20 to C. The network verifies and adds the transaction to the last block of the register:
- A’s account has $70.
- В – $10.
- С – $20.
- D – $0.
Security
If C wants to send $30 to user D after all payments have been made, the transaction will be denied. Network participants will see that C has only $20 in his account. The transaction will not be confirmed and will not be recorded in the ledger.
If someone destroys the ledger on the server, it can easily be restored. A copy of the register is available to all participants.
Decentralization
In public blockchains, information is stored on many computers located in different countries and cities. There is no specific party or authority to control the network.
Application variation
Anyone can create blockchain-based tools, products and services. This is not the case with centralized technology, whose development is more often limited to its initial idea.
Speed
Many companies – such as financial organizations that handle private data – are using blockchain to improve security and protect sensitive information. In addition, intermediaries often slow down transactions, so peer-to-peer networks seem to operate at a faster speed.
For example, a cryptocurrency transaction is faster than transferring a U.S. dollar through a bank. Blockchain transfers assets from one person’s digital account to another person’s account. A bank transfer is accomplished in several steps. Financial institutions must comply with laws and regulations to control these transactions. Third parties and regulators slow down the system.
Reduced costs
Blockchain attracts customers with low transaction costs because it is not tied to financial institutions that make money through transaction fees. The fee per payment does not depend on the volume of the payment.
Attracting investment
Blockchain also promotes the direction of long-term investments, allowing experimentation with a new funding model that differs from traditional capital raising activities (such as initial coin offerings – ICOs).
Making money from the technology
Blockchain is still in its infancy, but there is a global demand for engineers and developers in this field. Specialists in creating distributed ledgers are on the list of in-demand employees and rival designers of artificial intelligence, machine learning and IoT verticals. The average salary for a blockchain developer is 51.9% higher than the U.S. income norm.
Blockchain’s major drawbacks
Yet blockchains are not perfect. The main negative feature is that the technology lacks common protocols (TCP-IP, HTML and others).
Complexity of implementation
You can’t implement multiple blockchain protocols in one startup, hoping to add new features later without re-deploying or branching out(forks).
Lack of privacy
When information and verification on the blockchain is restricted to certain conditions, as in the case of private networks, there are no guarantees of privacy and security for users. In private blockchains, transactions can be censored due to corruption or collusion. In such networks, storage and computation may be distributed, but the nodes (servers) that verify the transfer of funds are centralized.
Unapproved transactions
Sometimes transactions are not accepted by part of the network, so are pending and cannot be included in the blockchain. This happens for the following reasons:
- Sending a small amount with insufficient fees. All bitcoin transactions require the miner fees to be validated by the network. If an insufficient fee is included, the transaction may never be confirmed. Therefore, it is unprofitable to transfer small amounts.
- Attempting to spend unconfirmed coins. Since distributed ledger technology prevents the same assets from being spent twice, cryptocurrencies that have not been confirmed by the network may hang up.
Scalability problem
This is another disadvantage of blockchain technology. The more people or nodes join the network, the more likely the chain is to slow down. Speeding up transactions is necessary for scalability – increasing the number of clients. But this is limited by network protocols.
Amount of data distribution
Blockchain registries are immutable. If each network participant keeps a full working copy of the network, then whenever new data is added, it will be written to the hard disks of all miners. Over time, information overloaded systems begin to run slowly.
For example, the average file size on a typical computer is 2MB, which is twice the current maximum size of an entire Bitcoin block, which contains more than 1,250 transactions. If 1,000 participants exchanged even one 2MB image over the network every day for an entire year, they would all have the blockchain taking up 730GB of data storage on their machines, totaling 730TB for the company as a whole. The problem is not the size of the storage medium, but trying to synchronize that amount of data in real time.
Not enough experts
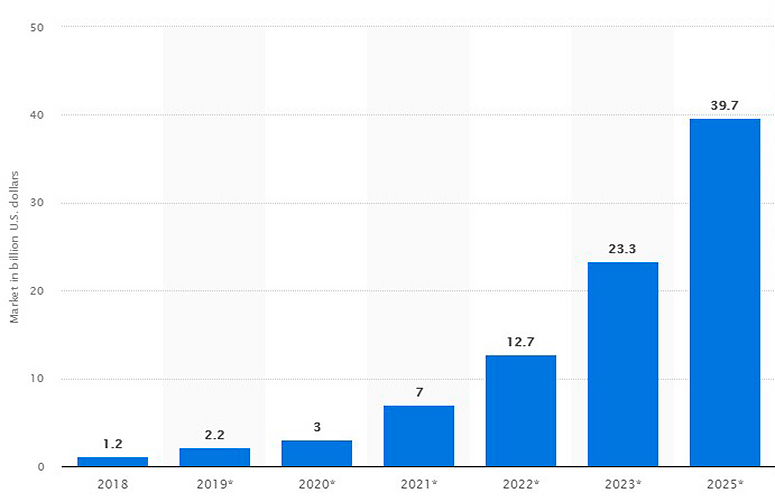
The blockchain industry is one of the few areas where demand for human resources exceeds supply. At the very beginning of the cryptocurrency market’s infancy, the number of developers of decentralized networks was 171 times less than the total number of programmers. The total decentralized networks market is expected to reach $39.7 billion by 2025. But it takes time to train professionals.
Applications today
Now that decentralized networks are spreading across many industries, the advantage of blockchain technology is becoming more evident.
Banking industry
Distributed ledgers have many chances to change the financial industry by eliminating intermediaries. To accomplish this, it is possible to:
- Create a decentralized ledger. As a result, the technology becomes the basis for faster payments with reduced fees.
- Launch clearing and settlement systems. Blockchain can reduce transaction costs and enable real-time transactions between financial institutions.
- Tokenize traditional securities (stocks, bonds and alternative assets) and place them on public blockchains. The technology can create more efficient and interoperable capital markets.
- Expand the operation of registries for loans and credits. By eliminating intermediaries, technology can make it safer to borrow money and lower interest rates.
- Provide customer verification and fraud prevention. By storing user information in decentralized blockchains, information sharing between financial institutions becomes secure.
Logistics
Controlling the distribution and delivery of goods is a complex process as the supply chain passes through many stages and locations. The sector also deals with masses of documents and invoices, and if even a single piece of paper goes missing, the delivery of the product may not be fulfilled.
Logistics companies are looking for new technologies to reorganize existing processes, reduce costs and increase transparency. Blockchain technology can track the performance history of manufacturers and suppliers. Companies can monitor carrier productivity, including on-time delivery.
Education
In both elementary school and university environments, grade auditing is a manual process. The adoption of blockchain solutions in the education sector can simplify verification procedures and reduce fraud associated with falsified diplomas and certificates.
Real estate
Pain points in buying and selling buildings, structures, land and other property include lack of transparency during and after transactions, an abundance of documents, potential fraud and errors in public records. With blockchain for real estate, property ownership can be recorded, tracked and transferred, relevant documents can be drafted, and liens can be recorded.
Healthcare
Hospitals suffer from the inability to securely capture reliable data. Quality information sharing will help make more accurate diagnoses and offer efficient and cost-effective treatment.
Law
Technology has various applications in the legal industry:
- Smart contracts.
- Land registry.
- Intellectual property rights.
- Supply chains.
- Litigation.
- Settlements and financial transactions.
For the foreseeable future, decentralized networks could change how law firms deliver services. Everything from escrow management to contract and transactional processes are already adapting and utilizing these tools.
The future of the technology
Blockchain is evolving rapidly. Innovations are constantly coming to market that are driving the technology’s proliferation in the global economy. Modern governance models will emerge that will allow corporations to approach decision-making in an efficient manner.
The trend in the market is that some startups will eventually fail, but the adoption of blockchain applications will continue. Perhaps, in time, national cryptocurrencies will emerge, integration of the technology into government agencies will increase, demand for blockchain developers will increase, and smart contracts will be applied in different areas of the economy.
Conclusion
Despite all the pros and cons of blockchain, the technology could revolutionize many industries and business processes in the future. However, implementation takes time and effort. Still, in the near future, we can expect governments to finally embrace the benefits of blockchain and use it to improve financial and public services.
Although some crypto startups will fail, people will gain more experience and knowledge on how to utilize this technology. Blockchain will encourage people to learn new skills, and traditional businesses will have to rethink their work processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
❓ How do I become a blockchain developer?
You need to take specialized courses.
🔎 What decentralized networks do businesses use in their work?
Companies develop private blockchains depending on their goals and objectives.
💡 Which sector is more likely to use blockchain technology?
Research has shown that the financial industry is the leader in blockchain adoption at work.
💻 How many nodes can be connected to the blockchain?
The number is not limited. However, the size of the network depends on its purpose.
🔑 Who owns the Bitcoin registry?
No one, however the network is managed by miners and a group of developers who have no control over the project.
Is there a mistake in the text? Highlight it with your mouse and press Ctrl + Enter
Author: Saifedean Ammous, an expert in cryptocurrency economics.














